February 22, 2023
 by Mary Clare Novak / February 22, 2023
by Mary Clare Novak / February 22, 2023
When it comes to investing, the options are overwhelming.
Plus, the returns aren’t always what you expect. If you've been lucky with investments and don't mind taking a risk, you may want to check out something exclusive and strategic, like a hedge fund.
And no, a hedge fund isn’t a piggy bank full of change to save up for a boundary of shrubs around your home. Hedge fund investors rely on investment portfolio management software to track and manage investment portfolios.
A hedge fund refers to pooled investments pulled by a partnership of accredited or institutional investors. Fund managers invest the accumulated funds in a variety of non-traditional assets for above-average returns. Managing these funds involves risk management and complicated portfolio construction.
When reading that definition above, it sounds as if hedge funds are just like any old investment. However, there’s a lot that sets them apart. Let’s go over the basics of hedge fund asset management to understand what makes them special and appealing to those looking for investment opportunities.
Hedge funds are known as alternative investments, meaning the characteristics of the funds, the strategy behind the investment, and the regulations overseeing the process set these funds apart from other financial activities. These funds use riskier strategies along and leverage assets while investing in options and futures derivatives. The real appeal of hedge funds lies in the reputation of managers who handle hedge fund investing.
Hedge fund managers often take hedged bets when investing, putting a portion of their assets in the opposite direction of the fund's focus to make up for any losses in core holdings. For example, hedge funds focusing on cyclical sectors like travel may invest a portion in non-cyclical sectors like energy to offset cyclical stock losses.
Tip: Getting your finance terminology mixed up? Learn the basics of a sinking fund to see how it's different from a hedge fund.
Here are the seven key characteristics that all hedge funds have, making it a unique investment opportunity.
The fee structure for hedge funds is often called Two and Twenty. Investors are charged a 2% management fee, regardless of the performance of the hedge fund. Then, they are charged a 20% performance fee only if the fund exceeds the hurdle rate. A hurdle rate is a minimum rate a hedge fund expects to earn on an investment.
Most hedge funds are structured as limited partnerships, and there are a couple of key players in the group.
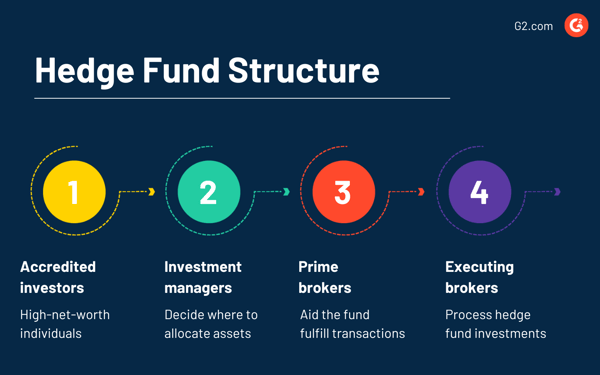
Hedge funds carefully evaluate and select investments that are likely to generate maximum profits. Below are four kinds of hedge funds that investors often explore.
While all hedge funds share the characteristics above, they can approach earning money a little differently.
There are two terms you need to know before we go over the strategies for hedge fund management.
A long/short equity hedge fund strategy is quite simple. Investors buy equities that are predicted to increase in value and sell those that are likely to decrease in value. One long trade and one short trade. It is common for investors to do this with two businesses in the same industry: invest in a predicted winner and loser. The profits of the money from the winner can be used to finance the losers. When done correctly, the fund will see a profit either way.
The market neutral strategy places equal value on the short and long trades in the market. Get it? They are neutral to the current conditions of the market. Investors match the positions they take on short and long stocks. So if one ends up doing better than the other, they win either way.
Arbitrage strategies attempt to take advantage of price differences between investments that are closely related. The process often involves using financial leverage.
In a merger arbitrage, an investor will take opposing sides in two companies that are currently merging. The stock is bought before the merger occurs, and the investor expects a return once it is over. However, they must take into account the fact that the merger might not close on time or at all.
A convertible arbitrage hedge fund is long on convertible bonds, or bonds that can be converted into shares, and short on the shares that those convertible bonds can become. This strategy attempts to profit off the inefficiencies of a business’s convertible bonds.
The fixed-income arbitrage strategy is a strategy where the hedge fund invests in both sides of opposition in the market to account for small price discrepancies. These hedge funds will keep an eye on fixed-income returns, like on government bonds. When they sense mispricing, they will take a long and short position, often with leverage, and then see a profit when the pricing is fixed in the market.
An event driven strategy includes hedge funds buying stock when prices inflate and deflate after a certain event, like a takeover or restructuring. These funds will sometimes purchase the debt of companies that are in financial distress or have gone bankrupt. They will first buy senior debt because it is the money that a bankrupt business must pay back first.
A credit hedge fund is another example of a fund that invests in the debt of other businesses. Investing in a credit focused hedge fund takes a great deal of knowledge in the debt side of the capital structure.
Global macro hedge funds invest in stocks, bonds, and currencies in an attempt to profit from the effect of political or economic events on a particular market. This process involves deep evaluations of the rise and decline of a nation’s economy. They position themselves to profit off a particular outcome of an economic or political event.
The short only method is basically trying to uncover accounting fraud or any misrepresentation of the value of stock in a financial statement.
Hedge funds make money by earning a flat fee along with a percentage of profits or positive returns that exceed the hurdle rate. The flat fee depends on the fee structure that investors pay on the basis of total assets under management.
The key difference is that: hedge funds are more aggressive and only available to accredited investors, whereas mutual funds are less risky and face trading restrictions.
Hedge funds leverage high-risk tactics like short selling stocks and taking speculative positions in derivative securities to generate higher returns regardless of the market conditions.
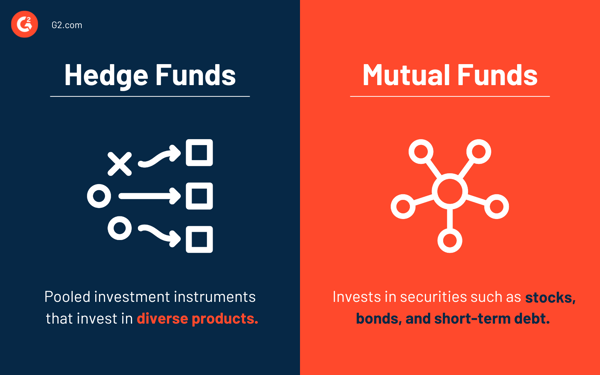
Mutual funds offer individual investors a cost-efficient way to create a diversified stock portfolio which may include publicly traded securities like bonds, stocks, or short-term investments. A mutual fund manager aims to outperform a benchmark index.
| Hedge funds | Mutual funds | |
| Investment objective | Maximize returns to increase performance fees | Outperform a benchmark index |
| Fees | 2% management fees and 20% of the profits | An expense ratio ranging between 0.5% to 2% |
| Shareholder requirements | Accredited investors only | Available to anyone |
| Liquidity opportunities | Every quarter, half-year, or sometimes longer | Easy to buy and sell except for funds with lock-in periods |
| Regulation | Not mandatory to register with the SEC | Mandatorily registered with the SEC |
While the manager of the hedge fund will see a profit no matter what, they still want that 20% performance fee. Also, a happy investor. Let’s go over some of the important parts of evaluating the success of a hedge fund.
Hedge funds must adhere to restrictions and regulations along with recordkeeping and trade reporting requirements of publicly traded securities. Many of the hedge funds in the U.S. are regulated by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), Commodity Pool Operators (CPO), and Commodity Trading Advisors (CTA).
The Regulation D under the Securities Act of 1993 restricts hedge funds to raise capital only in non-public offerings and from accredited investors with a minimum net worth of $1,000,000 or minimum income of $200,000.
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010 allowed the SEC to adjust the net worth and income standards as it deems appropriate for individuals. Banks and entities must have minimum total assets worth $5,000,000.
The Investment Company Act of 1940 also prohibits hedge funds from making public offerings and are subject to anti-fraud provisions as per the Securities Act of 1933 and Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
Hedge fund managers benefit from the Two and Twenty fee structure. While the 20% performance fee only helps them if they put the work in, the 2% management fee ensures they see a profit, no matter their amount of effort.
Let’s say a manager is working with a $100 million hedge fund. They could put their feet up and sip on a latte all day without working and still receive their 2%, which would be $2 million. That’s a pretty decent pay day.
However, just because these investors have a lot of money and feel like risking a little bit of it, doesn’t mean they accept an unorganized operation. Hedge fund managers will use financial services customer relationship management (CRM) software to make sure their investors feel taken care of.
Hedge funds avoid certain regulations that other investment vehicles are required to pay attention to, meaning they can engage in certain financial activities that are off limits to others. Hedge funds can maneuver these rules, so the managers and investors are barely taxed. This is why you must be an accredited investor or a high-net-worth individual to invest in a hedge fund.
A lot of hedge funds take advantage of carried interest, where the fund is treated and taxed as a partnership: the fund manager is the general partner, and then investors are the limited partners.
The fund manager’s income is taxed as a return on investment, not a salary.
However, when a hedge fund returns money to its investors, that return is subject to capital gains tax, which is a tax on the positive difference between an asset’s sale price and the original price at which it was purchased. There is a short term capital gains tax that applies to profits on investments held for less than one year. For investments held longer than one year, the capital gains tax can go as high as 20%.
To invest in hedge funds, you need to look for hedge funds accepting new investors. Besides using online tools to find these funds, you should always consult with trusted financial consulting providers who must have filed a Uniform Application for Investment Adviser Registration (ADV) form with the SEC. You’ll also need to verify that you’re an accredited investor. Plus, you may have to provide details of income, debts, and assets.
Check out the following best practices before you invest in hedge funds.
Big exhale. Hedge funds can get pretty complicated. With the different characteristics, strategies, tax regulations (or lack of), and controversies, understanding hedge funds is a lot to chew. However, if you are looking to make investment and you meet the requirements of the people that can invest, it can be a great source of income.
Check out the best financial research software for informed investment decision-making.
This article was originally published in 2019. It has been updated with new information.
Mary Clare Novak is a former Content Marketing Specialist at G2 based in Burlington, Vermont, where she is explored topics related to sales and customer relationship management. In her free time, you can find her doing a crossword puzzle, listening to cover bands, or eating fish tacos. (she/her/hers)
Real estate investing is your path to profit through property ownership.
.png) by Sam Radbil
by Sam Radbil
In the world of corporate bonds, risk management is everything.
 by Harshita Tewari
by Harshita Tewari
Real estate investing is your path to profit through property ownership.
.png) by Sam Radbil
by Sam Radbil



