September 18, 2020
 by Andrew DeBell / September 18, 2020
by Andrew DeBell / September 18, 2020
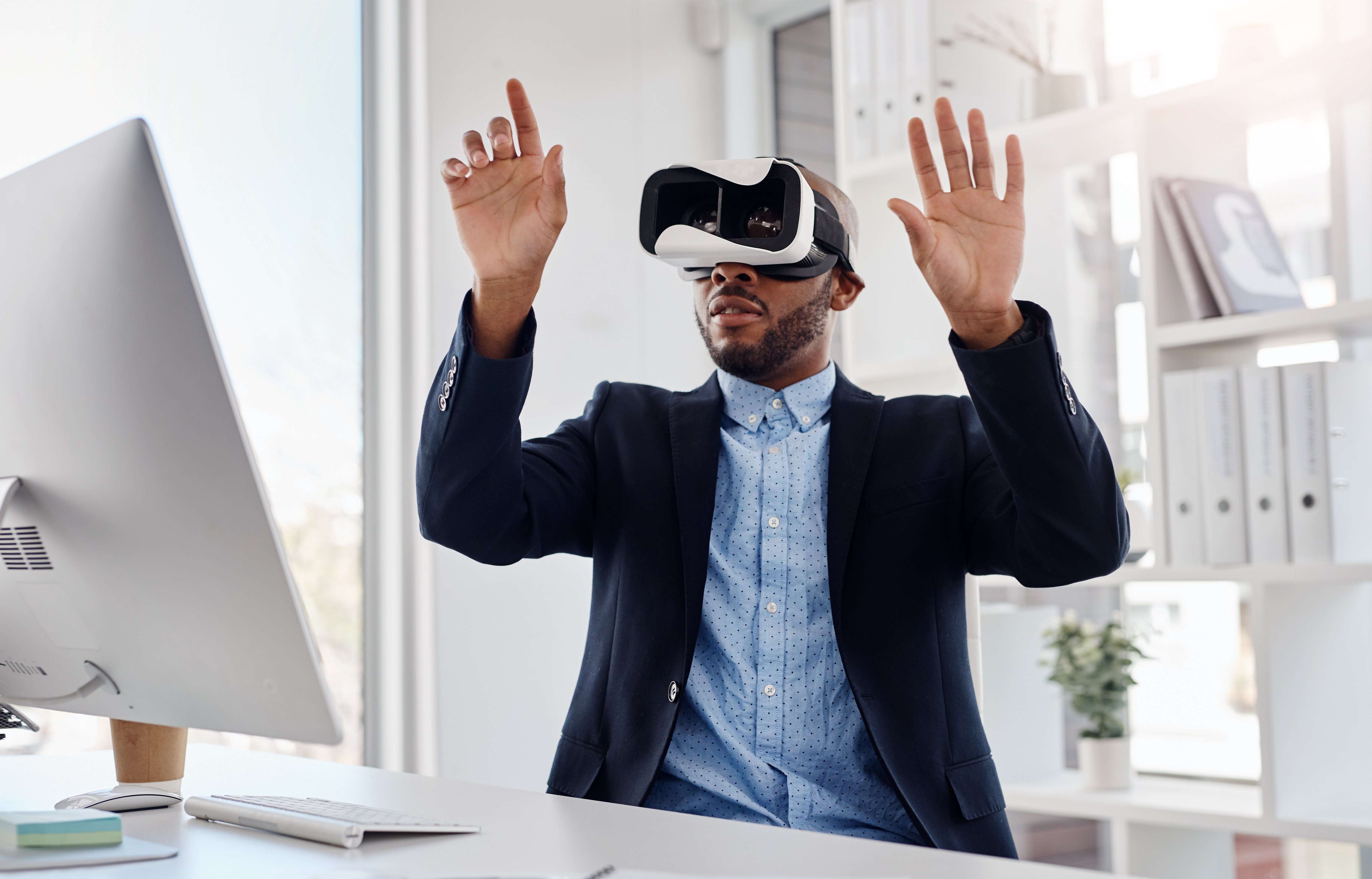

Imagine you work at a retail store. Black Friday is coming up and it’s time for your quarterly training.
Instead of the mundane PowerPoint your manager provided last quarter, she gives you a pair of fancy goggles to place over your eyes. And a controller to hold in your hands. You are instantly transported into a virtual 3D world. This world looks identical to the actual world. Your store is the same. People you work with. But it’s just actually just a digital representation.
In this virtual world, you experience the frenzy of a retail store on Black Friday. Crowds of families cramming through the doors. Aggressive customers arguing over TVs. Young kids screaming at their parents.
Although it’s just a simulation, it feels real. It feels like that teenage boy truly is upset. It feels like that old woman did get tripped by a combative family. How are you going to handle it?
Luckily, it’s all just for practice. This virtual experience is meant to train you for the real Black Friday. So when that blessed day does come in real life, you’ll be prepared to deal with any loose cannon customers thrown your way.
While this scenario may seem like a futuristic sci-fi tale, virtual reality (VR) training is being used by hundreds of organizations today. In fact, this exact scenario is based on an actual VR training program that Walmart has been using for store employees since 2017.
While the technology has been around for decades, only recently have corporations begun testing VR as a tool for training. And it makes sense. Research suggests that VR training provides better information retention and higher trainee engagement compared to traditional learning methods. VR training is one of the safest, controlled, reliable, and effective tools for humans to attain new knowledge and skills.
Virtual reality training is a 3D digital simulation of real-world scenarios for the purpose of learning.
Think of it as a fully immersive, interactive video game. Learners place a headset over their eyes. Hold a controller in their hands. Then are visually immersed into a virtual 360-degree environment.
Perceiving realistic sights and sounds, the virtual experience is often indistinguishable from the physical world. Learners interact with objects, locations, machines, tools, and even other people. These interactions allow learners to practice applicable skills and knowledge, without hazardous risks or expensive costs of failure.
Immersive virtual training provides an optimal environment for learning. Why? Humans learn best by physically performing a task, receiving feedback on mistakes, adjusting their strategy, and re-trying the task again. Many of these training experiences are too challenging to coordinate in the real world.
It’s too risky to have amateur surgeons use real patients to practice operations. Too environmentally damaging to burn down forests for firefighters to get reps. Too expensive to fly hundreds of global employees to a two-week training workshop.
VR solves these problems. In a virtually simulated scenario, a learner is able to repeatedly practice tasks exactly as they would in the physical world. Cost is fixed. Repetitions are unlimited. And research shows that employees retain two times more information from a VR training compared to training videos or text-based learning experiences.
The basis of VR learning effectiveness stems from a process known as sensory immersion. That is, immersing all of your senses into a virtual environment. If the virtual environment looks, feels, and sounds real, the human brain processes the information as though it were an actual, physical experience. It simply doesn’t know the difference.
VR technology is an absolute game-changer. Learning in this capacity has never been experienced in human history. It provides us with an opportunity to deepen our understanding of how the brain and neural networks interact. VR training could be a key to unlocking deep unsolved mysteries of the human learning process.
From Walmart cashiers to NFL quarterbacks, VR is used to upskill humans across many professions.
Notably dangerous or high consequence industries were early adopters of virtual training. Military, healthcare, manufacturing, to name a few. All professions where physical hands-on training is expensive and difficult to emulate. Where one minor mistake can lead to a deadly catastrophe.
VR training allows infantry soldiers to practice real-world combat missions. Heart surgeons practice high-risk operations on humans. And industrial plant operators practice safety protocols during a high-octane explosion.
But VR training isn’t only for high-risk professions. Many corporations around the world are using VR to upskill employees with more effectiveness and efficiency.
Large-scale U.S. retailers like Walmart are using VR to train in-store associates how to interact with customers. Associates slip on a headset and are transported into a virtual store where they can practice greeting people and learn how to deal with unhappy customers.
VR is also being used for new employee onboarding at tech companies like Lenovo. New employees can have an “in-person” session with the CEO. They can explore the company’s offices to get familiar with the departmental layout. They can see what clothes people wear and get a real-world sense for the company culture. Surveys from Lenovo employees have shown that after a VR onboarding, employees feel more motivated, excited, and empowered about joining their new company.
This new learning technology is also being used for employees to learn soft skills. Change management, leadership, empathy, and creativity are all high-demand skills amongst today’s workforce. Initial experimentation by PwC involved creating a training program that immersed employees into a content-rich learning experience. Employees were tasked with giving feedback to teammates, leading meetings, and dealing with difficult managers.
Their research found that employees learned soft skills four times faster than classroom training, were 275% more confident in applying skills, and four times more focused than their e-Learning peers.
Virtual reality training is used in a variety of industries, not just high-tech ones. A few we’ll go over in detail are military training, athlete training, and medical/surgeon training.
The U.S. Military uses VR to prepare individuals to be higher skilled and combat ready. They currently have VR training programs to upskill infantry soldiers, fighter pilots, and battlefield medics. It’s even being tested as a tool to help veterans recover from PTSD.
Training infantry soldiers is extremely costly, unsafe, and resource intensive. Battlefields are dangerous. Weaponry is expensive. Combat situations are life-threatening and therefore, difficult to replicate in real life.
Virtual reality simulations allow soldiers to train in an ideal environment. One that mimics a real-world battlefield, allowing soldiers to familiarize themselves with local terrain and interact with enemies. All with no risk of death or injury.
The U.S. Army has named their VR training for infantry soldiers the Synthetic Training Environment (STE). The idea is to maximize repetition. The platform allows soldiers to practice combat scenarios hundreds of times before hitting the battlefield.
Soldiers simply wear a VR headset and are instantly placed in a simulated enemy territory. The software emulates actual cities on Earth. Including detailed terrain, roads, and buildings. Soldiers are then tasked with completing real-world missions. Using artificial intelligence software called BISim, scenarios are randomized so each training situation is unique and unpredictable. This allows soldiers to prepare for the wide variety of fluctuating circumstances that real missions bring.
Fighter pilots in the Air Force are also being trained through VR. With an increasing demand for pilots, Air Force directors have been heavily experimenting with VR training to accelerate their pilot training pipeline.
New pilots strap on a VR headset and are transported into a fighter jet cockpit. All controls, switches, and displays are exactly as they would be in the actual jet. Pilots are then led through a training session by an instructor, verbally communicating instructions into the headset. The training program covers basic pilot skills like aerial barrel rolls all the way to advanced enemy combat scenarios. Many pilots that participate in VR training report real, physical sensations of excitement when they complete tasks.
Most recently, VR is being explored as a way to treat military veterans for PTSD. The technology leverages a well-known behavioral treatment for PTSD called exposure therapy. The idea is to slowly expose the patient to the exact situations they fear the most. For infantry soldiers, PTSD may have been caused by combat exposure. As a civilian, combat exposure is nearly impossible to replicate.
That is where VR training can help. Called virtual reality exposure therapy (VRET), patients are placed in a virtual environment. This environment can mimic any particular situation, helping an individual face their fears head on. Combat situations can’t be readily accessed in real life. VR provides safe, controlled exposures featuring jungles, helicopters, and scenarios that are causing harmful symptoms.
While this technology is new, the science appears to be promising. For Vietnam, Iraq, and Afghanistan War veterans, multiple studies have consistently shown a reduction in PTSD symptoms.
When VR is involved, patient feedback software can analyze patient feedback in order to improve satisfaction and ensure safety.
High-performing athletes in the NCAA, NFL, NBA, and Olympics are also jumping on VR technology for training.
Elite athletes succeed by being able to quickly recognize and react to situations. Virtual reality allows athletes to get unlimited repetitions, without the high cost and coordination of practice. Without taking a toll on the physical body. Unfortunately, many of the situations require high-impact practice to get repetitions. Football players smashing heads. Basketball players getting injured.
The Stanford college football team has been experimenting with VR training since 2014, especially for quarterbacks and defensive linemen. Players strap on a headset and are placed on a virtual field where they have to quickly recognize formations and make decisions. Compared to real-life practice, players can significantly increase their repetitions through VR. The more repetitions they get, the quicker they react on the field.
Professional football players in the NFL are also using VR technology to train. NFL quarterbacks are the most expensive players on the field. Managers can’t risk quarterback injury by putting them in high-risk practice situations on the field. VR training provides a worthy alternative.
Quarterbacks are immersed in a virtual setting where they wear a real football helmet and have room to run around, just as they would on an actual football field. The quarterback has to read the defense, call audibles, and make accurate throws to receivers.
The best part? They can run hundreds of repetitions without tiring out teammates or risking any injuries of other players. These game-like scenarios allow quarterbacks to form long-term muscle memory they can bring with them to the field on gameday.
Professional NBA basketball players, particularly on the Washington Wizards, have used VR training to accelerate learning. The technology has been especially useful in helping with free throw shooting, allowing players to gain confidence before stepping onto the court.
Medical device technology has radically improved over the past 50 years. With any new device comes challenges training people how to use it.
This is a sizable challenge when it comes to new surgeons, where up to 30% of graduating surgeons are not adequately prepared to operate independently. And worse, medical errors are the third leading cause of death in the U.S.
With an aging population and increased future demand for surgeries, VR training is coming to the rescue. Some residency programs are using virtual hands-on training to simulate an operating room environment. Surgeons interact with realistic tools and have a checklist of tasks to complete – just one way AI functionalities are working in healthcare.
Not only does VR training help surgeons practice repetitions. The technology also provides real-time feedback to gauge surgical competence. Rather than relying on the archaic method of human subjectivity, VR technology provides accurate data points on what surgeons have done correctly and what areas need more improvement.
Although research around VR training and surgery is still in its infancy, there have been pilot studies showing incredibly promising results. A surgical training study at UCLA showed that a VR-trained group scored 130% higher in accuracy compared to peers that studied with traditional methods. They also found that the VR-trained group completed 38% more steps correctly, at a 20% faster speed. VR surgical training appears to be promising for the future.
Here are six benefits that virtual reality training is bringing to various industries.
Repetition is key to learning. Through continued practice, skills become progressively easier over time as the knowledge transfers from conscious to subconscious. NFL quarterbacks can run unlimited reps without tiring out receivers. Brain surgeons can practice on hundreds of patients without the worry of injury. VR training allows for unlimited repetition. Continual on-the-job practice that helps radically improve skill attainment.
Hands-on experience is essential for human learning. People only remember 10% of what they read, but remember 90% of what they do. Active learning by performing the real task in the actual environment.
VR training provides a fully immersive experience. The learner is placed into a lifelike scenario. Surrounding objects, tasks, and locations are identical to the real world. Their brain tricks them into thinking the experience is real. By performing actual tasks in a virtual space, knowledge retention is rapidly increased. The learning experience through virtual reality is unrivaled compared to any traditional format.
Many on-the-job skills can be dangerous to practice. Pilots learning how to fly fighter jets. Mechanics learning to operate high-risk machinery. VR creates a no-risk environment for training. It’s safe and fully controlled without any risk of injury.
Pilots can attempt to fly without the fear of crashing. Mechanics can operate machinery without the risk of malfunction. All situations that would typically be unsafe can be practiced safely in a virtually controlled environment.
Recent research shows that memory retention is two times higher from a VR experience compared to traditional text-based learning materials. This could be because the human mind creates mental constructs by the way they perceive and move. VR training seems to improve information retention by tapping into a person’s spatial awareness – the position of their body and the way they move about the world.
VR training can be completed and repeated anytime, anywhere. At your desk? Pop on a headset and start learning. On-the-job at a manufacturing plant? See how it’s done by immersing yourself into a virtual setting.
Training is now accessible anywhere. The technology eliminates all time and location constraints compared to traditional classroom learning. And with adaptable software, new training programs can be uploaded and distributed to thousands of employees with the touch of a few buttons.
Traditional corporate training is expensive. Companies must exhaust mounds of cash for employees to travel across the globe for in-person workshops. Hotels, airfare, food. These all come at a steep price.
VR training offers a worthy alternative. When VR first launched, the technology was also expensive and difficult to implement at scale. Today, the cost is more reasonable. Headsets can be purchased for less than $1,000 and can be used to train employees for four or more years.
While the upfront investment is initially higher than traditional learning methods, it can save money over the long-term. According to research by PwC, if an organization has 3,000 learners, VR training is 52% more cost effective than classroom training. The more employees trained; the higher return VR training provides.
Here are three companies already using VR training to make the lives of their employees easier.
Before an astronaut can ship off to space, they must complete two years of training on Earth. As you can imagine, the unique environment of space is difficult to replicate on Earth. To combat this challenge, NASA uses VR to train astronauts for upcoming missions.
Located in Texas, NASA has an entire Virtual Reality Lab dedicated to VR training. Here, astronauts plan their expeditions in and around the International Space Station. Of course, it’s all virtually simulated.
The program helps astronauts understand the scale and locations within the ISS. They learn skills like how to properly grip the handrails. And where to locate specific compartments of the station.
It also helps astronauts practice emergency drills. Life-threatening situations like losing connection from the ISS or floating freely away in space, are common scenarios astronauts need to prepare for. With VR, astronauts have a safe, controlled environment to practice. And with the benefit of endless repetition, ensure they’ve mastered the critical skills before beginning the high-risk journey into space.
Across the U.S., Walmart retail stores have over 17,000+ VR headsets to help train store associates. Over 1.4 million employees were trained with VR. Topics ranging from hands-on technology training to Black Friday prep (as we mentioned earlier).

Andy Trainor, Walmart’s Senior Director of Walmart Academies, said, “The great thing about VR is its ability to make learning experiential. When you watch a module through the headset, your brain feels like you actually experienced a situation.”
How have the results been so far? Walmart’s VR training appears to improve retention and task confidence. Compared to their prior training, exam scores improved by 10-15%.
With these impressive pilot program results, Walmart continues to invest in VR training. They expanded their topics to focus on three core areas: technology, soft skills, and compliance. Technology training is being used to help associates learn how to perform tasks on new equipment such as POS machines, or self-service kiosks.
While these programs do benefit Walmart, the company is happy to provide a technology that enriches the careers of their associates for the long-term.
Armed robberies are a common crime at cell phone retailers like Verizon. When a thief enters your store and tries to steal an iPhone, how should you react?
Traditional text-based training doesn’t provide associates with the urgency needed to make these critical split-second decisions. Reading a PDF about cellphone thieves isn’t likely to prepare you for the real event.
What method can prepare you? VR training. Verizon set out to help their frontline associates learn how best to handle dangerous situations, like armed robbery. How to keep calm, follow protocol, and avoid escalation.
Using actual theft footage captured from security cameras, the Verizon L&D team built three VR training scenarios. Store associates were immersed into these scenarios where they had to react to thieves entering their store and attempting to steal merchandise.
Many associates reported their hearts racing, feeling true emotions as if they had experienced an actual robbery. In a post-training survey, 97% of employees felt prepared to take on a dangerous situation at their store. That high level of confidence is nearly unmatched to what an employee would feel like without the proper training.
With the success of this program, Verizon also plans to extend their VR training to other departments. Customer service, communication, and empathy are all high-priority topics for improving employee skills.
It’s safe to say VR training is here to stay. Hundreds of organizations have seen success with this safe, reliable, and effective medium for learning. With improved learner retention and engagement, why wouldn’t your L&D department jump on board? With a projected forecast of 48%+ growth in the next five years, VR is merely at the dawn of its potential. Prepare yourself for the future of training as we enter a world of unlimited possibility.
Discover all of the latest virtual reality software on the market today and see how you can bring VR training to your work environment as a next step toward safer, more innovative training processes.
Andrew DeBell is a creative training consultant and digital marketing strategist at Water Bear Learning. He helps organizations communicate with their internal audiences through digital media, visual design, and interactive learning.
Cross-validation is an invaluable tool for data scientists.
 by Amal Joby
by Amal Joby
“Congrats on joining the sales team! Here’s a 94-slide deck and a link to some old Gong calls....
 by Harshita Tewari
by Harshita Tewari
The relationship between customer and representative can be a beautiful thing.
 by Alexa Drake
by Alexa Drake
Cross-validation is an invaluable tool for data scientists.
 by Amal Joby
by Amal Joby
“Congrats on joining the sales team! Here’s a 94-slide deck and a link to some old Gong calls....
 by Harshita Tewari
by Harshita Tewari