October 13, 2025
 by Samudyata Bhat / October 13, 2025
by Samudyata Bhat / October 13, 2025

“Let's get to the root of the problem."
That’s the best approach to finding complex business solutions. Getting to the bottom of any issue is crucial, even if you can't pinpoint the exact problem at first.
Firms often use log analysis software containing detailed information records to identify and analyze different circumstances that arise in the workplace. However, if you’re feeling lost, try a root cause analysis template to help you understand the situation and develop feasible solutions to complex problems.
A root cause analysis (RCA) template is a structured form used to document and analyze the underlying causes of a problem. It helps teams outline the issue, identify root causes using tools like the 5 Whys or fishbone diagrams, and record corrective actions to prevent recurrence.
Certain RCA methodologies are focused and specific, while others concentrate on generic strategies. People often use an RCA to learn more about why a system performs differently from or outperforms similar methods. Most of the time, however, the attention is on specific issues, particularly when they involve critical systems.
An RCA evaluates all contributing elements and connects events meaningfully to address problems and prevent them from recurring. It’s only possible to determine how, when, and why the issue occurred by focusing on the root cause rather than its surface indicators.
RCA is exceptionally vital since it identifies core flaws in a product’s development process, allowing teams to take the proper corrective action to prevent troubles from happening in the future. As a result, the finished product has fewer flaws and needs less reworking.
For instance, adding more team members is a quick solution if your business needs to improve its employee retention rate. But by using RCA, you may discover why team members are leaving your organization and apply that information to improve employee retention. Low retention rates might have one of the following root causes.
A company can use research to identify one or more root causes after considering the possible reasons. You can’t find a lasting solution until you know the underlying issues. An RCA template employs a systematic approach to problem-solving, rather than applying a band-aid and hoping for the best.
A root cause analysis template simplifies the root cause analysis process by allowing you to visualize your problem and its underlying causes in a graphical format. RCA can be done via various methods, each appropriate for different situations. Discussed below are the most common root cause analysis templates.
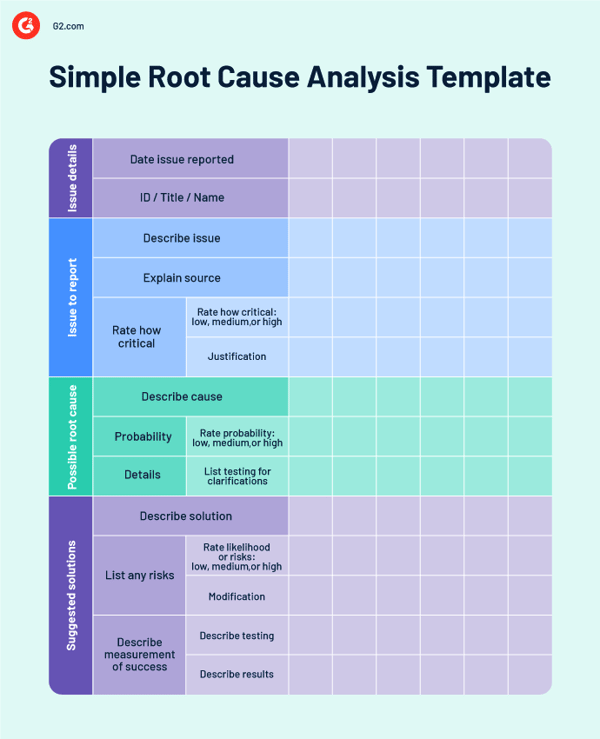
Simple RCA templates look at issues that don't need in-depth examination. You can use it to briefly describe the issue or problem, a list of probable causes, prospective solutions, and a conclusion as to whether or not those solutions were effective.
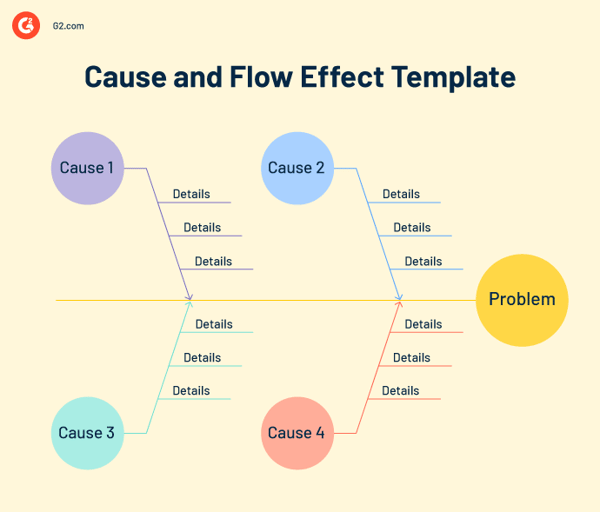
This flowchart categorizes the issue into symptoms, potential causes, and natural causes to facilitate a logical solution. Cause-and-effect flowcharts are often drawn using a structured fishbone or tree diagram. The fishbone diagram displays the problem or effect at the head or mouth of the fish, while a tree diagram branches out the list of root causes.
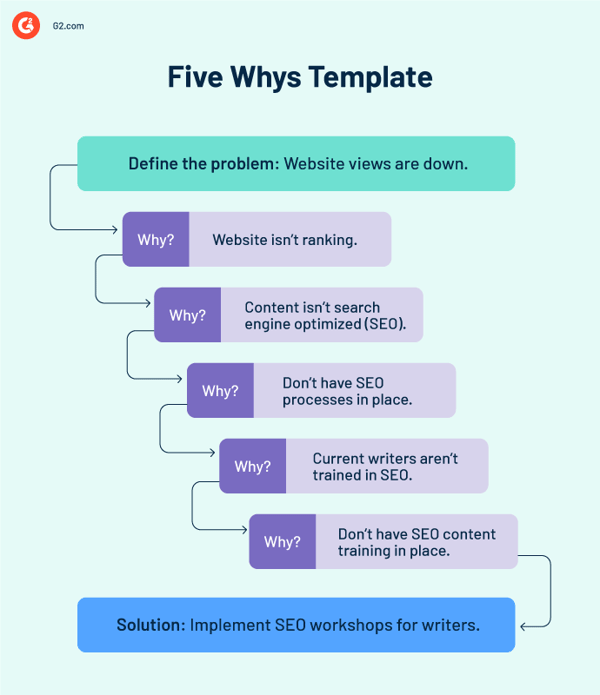
The 5 Whys method may identify the underlying causes of issues. Ask "why" instead of accepting the case at face value until you recognize a procedure or system that isn't operating as it should. You might uncover hidden levels of problems by not settling for those initial solutions.
A 5 Whys root cause analysis template typically includes questions or prompts to help you identify the underlying causes of the situation. A simple Five Whys root cause analysis template may look like this:
Because the approach is iterative, you may trace the problem back to its core cause and design effective ways to solve it by answering these questions. You may add questions or customize the template to fit specific problems and requirements.
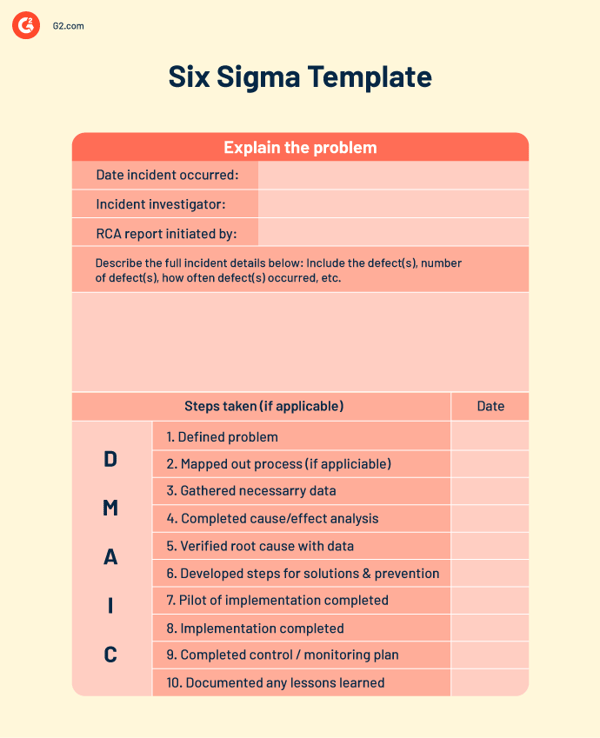
Six Sigma DMAIC is a way to minimize mistakes and improve business processes. It has its method of examining and examining fundamental causes. The abbreviation "DMAIC" alludes to the phases in this procedure:
Define and measure: What was anticipated, and what went wrong instead? What occurred, when, and where did it happen? What is the significance of the situation, and who was affected?
Analyze: Examines the cause-and-effect links between the components contributing to the problem. What caused the situation, and what must be done to prevent it from recurring?
Implement and control: What are viable solutions to the problem, and what are the causes and advantages of putting them in place? How can solutions be monitored and regulated to prevent the problem from recurring?
This root cause analysis template guides you through each of the preceding processes and allows you to add information regarding the root cause action plan, resolution, and investigation team. Furthermore, this root cause template contains diagrams that may be used to depict how various contributing components (for example, people, processes, and equipment) link to one another and to the problem itself.
The cause mapping template combines the simple root cause analysis template, the Six Sigma DMAIC template, and the 5 Whys root cause analysis template. It contains a thorough issue summary, a timetable, an analysis of the "why" question, illustrations to clarify the process, sections for suggesting and assessing alternative solutions, and a section for developing an action plan.
Download a free root cause mapping template from Smartsheet.
| Method | Best For | Pros | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 Whys | Simple, recurring issues | Quick and easy | May oversimplify complex problems |
| Fishbone (Ishikawa) | Process or system-wide problems | Visual and collaborative | It can become messy with too many variables |
| FMEA | Manufacturing or engineering | Prioritizes failure impact | Data-heavy, time-consuming |
| DMAIC (Six Sigma) | Process improvement | Structured and data-driven | Requires trained personnel |
| Cause Mapping | Cross-functional problem solving | Holistic, ties causes to effects | Needs clear event data |
A variety of techniques are used to determine the root causes in RCA. Below are some steps you can follow to help identify issues through the RCA process.
To begin a root cause analysis, you must first characterize the problem in real-time. If you have several issues to fix, start with one and do numerous RCAs to find answers. Focusing on one issue at a time will give you a higher chance of swiftly determining and resolving the root cause of the problem.
Identifying your problem also entails ensuring that everyone is on the same page.
Data collection is necessary to illustrate the issue. You can use the company's research resources to comprehend the issue's signs and symptoms better. During this phase, you should inquire about the following:
You can come up with plausible reasons for the problem after gaining a better understanding of how it affects your business and network.
The most crucial step in the root cause analysis method is identifying potential root causes and drawing out a root cause analysis template. RCA templates help in better data visualization and a clearer understanding of your problem. A solution and action plan will ultimately emerge from the causes you identify in this stage. Popular root cause analysis templates for solving obstacles include Pareto charts, simple root cause analysis, cause-and-effect diagrams, the 5 whys technique, and cause mapping.
You'll need to go through as many probable root causes as possible to find your problems underlying cause. If you've explored all possibilities, consider the following:
You may use several root cause analysis methods for effective solutions. Among these strategies are:
To get to the root cause of a trend, analysts often use alternative processes such as data discovery and data mining to create a root cause analysis report.
Professionals who want to focus on root cause analysis and continuously improve reliability should be able to select the most suitable approach for each situation. Streamlining an action plan with a single root cause analysis template is ideal, but often multiple strategies are needed in a report template to address a problem.
After identifying the fundamental problems you've uncovered, it's time to find answers and take action. Your solutions should target the actual cause, but as a consequence, they will work their way back up the chain and fix your original problem.
When you're ready to begin developing your implementation strategy, ensure it's streamlined and shared in a tool all stakeholders can access. Project management software lets your team interact easily and arrange deliveries as needed.
RCA helps resolve persistent project problems and significant bottlenecks in corporate operations. Some of its beneficial business impacts are discussed below.
The following are some challenges that may be encountered during the RCA process.
Root cause analysis methods combine human inference with data collection and reporting tools. To conduct the RCA process, IT teams often turn to the platforms they already use, as they often contain data likely to provide deeper insights into the defined problem. These tools may include:
Many of these solutions have root cause analysis tools built directly into their platforms. In addition, some vendors offer tools that collect and correlate information from many platforms to help troubleshoot problems or failures. For example, automation tools with artificial intelligence for IT operations (AIOps) capabilities can learn lessons from past occurrences and suggest future corrective actions.
Analysts should employ the techniques and resources most suitable to their specific set of circumstances while conducting an RCA.
Troubleshooting addresses immediate symptoms, while RCA digs deeper to eliminate the underlying issue. RCA ensures problems don’t resurface, whereas troubleshooting focuses on short-term fixes.
A basic RCA can take a few hours, while complex, data-driven investigations may require several weeks to complete. Timelines depend on system complexity, stakeholder input, and the quality of the data.
Yes. Modern RCA tools, combined with AIOps and machine learning, can automatically identify patterns, correlate events, and suggest probable causes, thereby accelerating diagnosis and enhancing accuracy.
RCA is widely used in manufacturing, IT operations, healthcare, finance, and human resources, anywhere process reliability and quality improvement are priorities.
Successful RCA results in measurable reductions in recurring issues, improved process reliability, shorter downtime, and stronger stakeholder confidence.
RCA may be used in practically every circumstance. Choosing how far to pursue your research involves sound reasoning and good judgment. It is also crucial to plan ahead and forecast the repercussions to your solution. This helps you identify potential problems before they happen.
RCA does not produce immediate solutions, but getting to the root cause of an issue nips it in the bud permanently.
If RCA methods have piqued your interest, explore how you can perform statistical analysis for scientific decision-making!
This article was originally published in 2023. It has been updated with new information.
Samudyata Bhat is a former Content Marketing Specialist at G2. With a Master's degree in digital marketing, she specializes her content around SaaS, hybrid cloud, network management, and IT infrastructure. She aspires to connect with present-day trends through data-driven analysis and experimentation and create effective and meaningful content. In her spare time, she can be found exploring unique cafes and trying different types of coffee.
Root cause analysis (RCA) brings together training, tools, and technology to assist...
 by Sebastian Traeger
by Sebastian Traeger
The G2 Gives review campaign is an initiative that allows users to support charitable causes...
 by Keshav Pushadappu
by Keshav Pushadappu
What if there was a way to support nonprofits and boost your brand awareness?
 by Lauren Pope
by Lauren Pope
Root cause analysis (RCA) brings together training, tools, and technology to assist...
 by Sebastian Traeger
by Sebastian Traeger
The G2 Gives review campaign is an initiative that allows users to support charitable causes...
 by Keshav Pushadappu
by Keshav Pushadappu


