What is an ERP System? Understanding the Basics
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become the backbone of modern businesses, serving as comprehensive software solutions that integrate and manage core processes across an organization. In 2025, these systems have evolved into sophisticated platforms that leverage artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced analytics to drive efficiency and informed decision-making.
At its core, an ERP system functions as a centralized database and operational hub, offering real-time insights and automation capabilities. Key aspects of modern ERP systems include:
- Seamless integration of core business functions such as finance, human resources, manufacturing, supply chain, and customer relationship management
- Real-time data sharing and collaboration across departments and geographical locations
- Advanced automation of routine tasks and complex workflows using AI and machine learning algorithms
- Predictive analytics and data-driven insights for strategic decision-making
- Scalability to adapt to business growth and changing market conditions
- Enhanced security features to protect sensitive business data
The evolution of ERP systems traces back to the 1960s with the development of early inventory management and control systems. Over the decades, these systems expanded to include more business functions, eventually leading to the comprehensive, cloud-based ERP platforms we see today.
How ERP Systems Function in Modern Businesses
In today's fast-paced business environment, ERP systems play a crucial role in:
-
Streamlining operations by eliminating redundant processes and manual data entry, leading to increased productivity and reduced errors
-
Enhancing decision-making through real-time, data-driven insights and AI-powered recommendations, allowing businesses to respond quickly to market changes
-
Facilitating seamless collaboration across departments, locations, and even with external partners, breaking down information silos
-
Ensuring regulatory compliance and robust data security in an increasingly complex legal landscape, reducing risk and potential penalties
-
Providing a scalable foundation for business growth, digital transformation, and innovation, enabling companies to stay competitive in rapidly evolving markets
-
Improving customer satisfaction by providing a unified view of customer interactions and enabling personalized experiences
-
Optimizing supply chain management through real-time visibility and predictive analytics, reducing costs and improving efficiency
By integrating various business processes, ERP systems create a single source of truth for organizational data. This integration allows for more accurate forecasting, better resource allocation, and improved overall efficiency across the entire business ecosystem.
Core Components of an ERP System
While ERP systems can vary in their specific offerings, most include these fundamental components:
- Financial Management: Advanced general ledger, accounts payable/receivable, budgeting, and financial reporting with AI-driven insights for improved financial planning and analysis
- Human Resources: Comprehensive HR management including payroll, talent management, and employee experience platforms, with AI-powered recruitment and performance analytics
- Supply Chain Management: End-to-end visibility and control over procurement, inventory, and logistics with predictive analytics for demand forecasting and risk management
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Unified customer data management, sales automation, and personalized marketing capabilities, enhanced by AI for customer behavior prediction and sentiment analysis
- Manufacturing: Smart production planning, quality control, and work order management with IoT integration for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance
- Business Intelligence: Advanced reporting, analytics, and data visualization tools powered by machine learning for actionable insights and trend identification
- Project Management: Comprehensive tools for planning, executing, and monitoring projects, with resource allocation optimization and real-time progress tracking
- Asset Management: Tracking and management of physical assets throughout their lifecycle, including maintenance scheduling and depreciation calculations
These components work in harmony to provide a holistic view of business operations, facilitate seamless collaboration, and enable organizations to optimize processes, reduce costs, and drive growth in an increasingly competitive landscape. The integration of these modules allows for seamless data flow and process automation across different business functions, eliminating data silos and improving overall operational efficiency.
As we explore specific ERP system examples in the following sections, we'll see how different vendors implement these core components and offer unique features to address various industry needs and business sizes in 2025 and beyond. The continuous evolution of ERP systems, driven by advancements in AI, IoT, and cloud computing, promises even greater capabilities for businesses to streamline operations, gain competitive advantages, and adapt to rapidly changing market conditions.
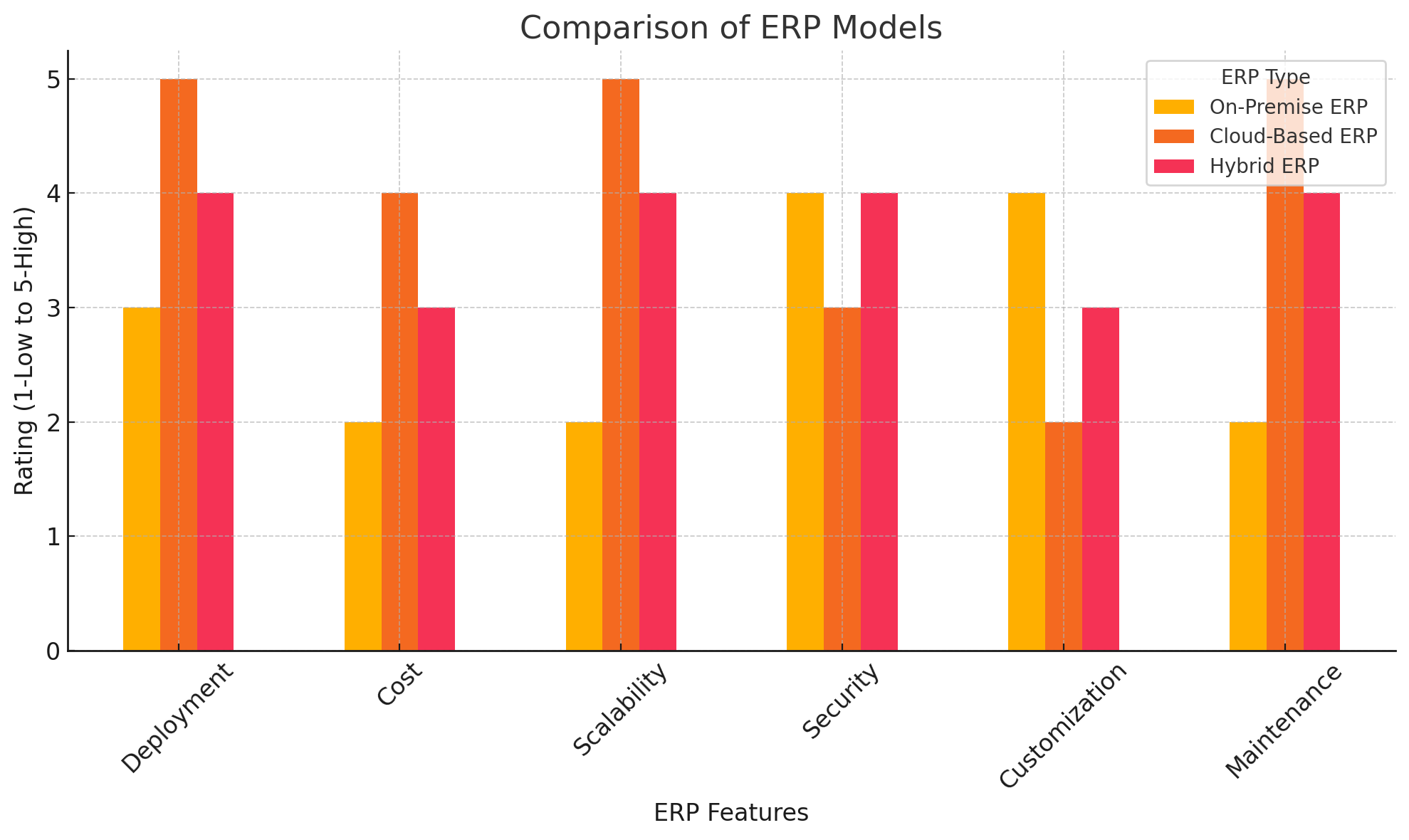
Types of ERP Systems: On-premise, Cloud-based, and Hybrid Solutions
In 2025, the ERP landscape offers a variety of deployment models to suit different business needs, IT strategies, and regulatory requirements. Each type of ERP system has its own set of advantages and considerations. Let's explore the three main types of ERP systems: on-premise, cloud-based, and hybrid solutions.
On-premise ERP Systems
While less common in 2025, on-premise ERP systems still play a role for organizations with specific security or compliance needs. Key characteristics include:
- Complete control over data and infrastructure, allowing for customized security measures
- Extensive customization capabilities to meet unique business requirements
- Higher upfront costs for hardware, software licenses, and IT staff
- Longer implementation times due to hardware setup and software configuration
- Responsibility for maintenance, upgrades, and security management
- Limited accessibility from outside the organization's network without additional infrastructure
On-premise solutions are typically favored by large enterprises in highly regulated industries or those with unique operational requirements that can't be met by standardized cloud offerings. Industries such as defense, certain government agencies, and some financial institutions often opt for on-premise solutions due to strict data sovereignty and security requirements.
Cloud-based ERP Systems
Cloud-based ERPs, also known as Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions, have become the dominant model in 2025. These types of ERP systems offer numerous benefits:
- Lower upfront costs and predictable subscription-based pricing, making ERP accessible to smaller businesses
- Rapid implementation and easy scalability to accommodate business growth
- Automatic updates and maintenance are handled by the vendor, ensuring access to the latest features and security patches
- Accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection, supporting remote work and global operations
- Enhanced collaboration features for remote and distributed teams
- Built-in AI and machine learning capabilities leveraging the cloud's processing power
- Improved disaster recovery and business continuity through cloud-based backups and redundancy
The shift towards cloud-based ERPs has democratized access to sophisticated business management tools, particularly benefiting small and medium-sized enterprises. Industries such as retail, professional services, and technology startups have been quick to adopt cloud-based ERP solutions due to their flexibility and lower total cost of ownership.
Hybrid ERP Solutions
Hybrid ERP systems combine elements of both on-premise and cloud-based solutions, offering a flexible approach for businesses with specific needs or regulatory requirements. Advantages of hybrid solutions include:
- Ability to keep sensitive data on-premise while leveraging cloud capabilities for other functions
- Gradual migration path from legacy systems to cloud infrastructure, allowing for phased implementation
- Customization of deployment based on individual module requirements and data sensitivity
- Potential for better integration with existing on-premise systems and legacy applications
- Flexibility to adapt to changing regulatory landscapes and data residency requirements
- Balancing of performance needs between local processing and cloud scalability
Hybrid solutions provide a balance between control and flexibility, making them an attractive option for businesses in transition or with complex IT environments. Industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and certain financial services often opt for hybrid solutions to maintain control over critical data while benefiting from cloud capabilities in other areas.
Factors Driving the Shift to Cloud-based ERP
Several factors have accelerated the adoption of cloud-based ERP systems in 2025:
-
Cost efficiency: Reduced need for in-house IT infrastructure and staff, lowering total cost of ownership
-
Scalability: Easier to adjust resources based on business growth or seasonal demands, providing flexibility
-
Remote work support: Cloud-based systems facilitate collaboration for distributed teams, essential in the post-pandemic work environment
-
Continuous innovation: Regular updates ensure access to the latest features and security enhancements without disruptive upgrades
-
Focus on core competencies: Outsourcing ERP management allows businesses to concentrate on their primary activities and strategic initiatives
-
Advanced AI and analytics: Cloud platforms offer more powerful computational resources for AI-driven insights and predictive analytics
-
Sustainability: Cloud data centers often have better energy efficiency, aligning with corporate sustainability goals and reducing carbon footprint
-
Global accessibility: Cloud-based systems enable seamless access for global operations and mobile workforces
-
Integration capabilities: Easier integration with other cloud-based services and third-party applications, creating a more connected ecosystem
-
Disaster recovery: Improved business continuity through robust backup and recovery options provided by cloud vendors
As we dive into specific ERP examples in subsequent sections, we'll see how vendors are leveraging these deployment models to meet diverse business needs and industry requirements in 2025 and beyond. The choice between on-premise, cloud-based, or hybrid ERP solutions depends on various factors including business size, industry regulations, existing IT infrastructure, and long-term strategic goals. Organizations must carefully evaluate these options to select the deployment model that best aligns with their unique requirements and future growth plans.
Common ERP Modules and Their Functions
In 2025, ERP systems have evolved to offer a comprehensive suite of modules that cater to various business functions. These modules work together seamlessly to provide a holistic view of an organization's operations. Let's explore the core modules that make up a modern ERP solution:
Financial Management
The financial management module remains the cornerstone of ERP systems, now enhanced with AI-driven capabilities:
- AI-powered general ledger and chart of accounts for automated reconciliation and real-time financial visibility
- Predictive accounts payable and receivable management with automated invoice processing and payment optimization
- Real-time cash flow management and forecasting using machine learning algorithms
- Multi-currency and multi-entity support with blockchain integration for secure cross-border transactions
- Advanced financial reporting and compliance with automatic regulatory updates and AI-assisted audit trails
- Fraud detection and prevention using machine learning algorithms to identify anomalies and potential risks
- AI-driven budgeting and forecasting tools that incorporate external economic indicators and market trends
- Automated tax management and reporting with real-time updates to tax regulations across multiple jurisdictions
Human Resources Management
Modern HR modules have expanded to encompass the entire employee lifecycle, leveraging AI and analytics:
- AI-driven recruitment and talent acquisition with predictive candidate matching and bias reduction
- Predictive workforce planning and analytics to optimize staffing levels and skills mix
- Personalized learning and development platforms with AI-recommended training paths
- Employee experience management with sentiment analysis and real-time feedback mechanisms
- Advanced performance management and goal-setting tools with continuous feedback loops
- Automated compliance management for global workforce regulations and labor laws
- AI-powered employee retention strategies with predictive attrition modeling
- Virtual and augmented reality integration for immersive onboarding and training experiences
- Wellness and mental health tracking with personalized support recommendations
Supply Chain Management
Supply chain modules have become increasingly sophisticated, leveraging IoT, AI, and blockchain technologies:
- AI-powered demand forecasting and inventory optimization with real-time market data integration
- Real-time supply chain visibility with IoT integration for tracking and tracing
- Automated procurement and vendor management with AI-driven supplier selection and risk assessment
- Blockchain-enabled traceability and authenticity verification for enhanced transparency
- Predictive maintenance for logistics and warehouse operations using IoT sensor data
- Sustainability tracking and carbon footprint management across the entire supply chain
- AI-optimized route planning and logistics management for cost and time efficiency
- Autonomous warehouse operations with robotics and AI integration
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM modules now offer hyper-personalized customer experiences powered by advanced analytics:
- AI-driven lead scoring and opportunity management with predictive win probability
- Predictive sales forecasting and pipeline management using historical data and market trends
- Omnichannel customer service with natural language processing for intelligent chatbots and voice assistants
- Personalized marketing automation and campaign management with AI-optimized content and timing
- Customer analytics with real-time sentiment analysis across multiple touchpoints
- Augmented reality integration for virtual product demonstrations and interactive catalogs
- AI-powered customer segmentation and lifetime value prediction
- Social media integration with AI-driven sentiment analysis and trend detection
- Predictive customer churn modeling with proactive retention strategies
Manufacturing and Production
Manufacturing modules have embraced Industry 4.0 technologies for smart manufacturing:
- Digital twin integration for real-time production monitoring and simulation
- AI-optimized production planning and scheduling with dynamic adjustments
- IoT-enabled quality management and control with predictive defect detection
- Predictive maintenance for equipment and machinery to minimize downtime
- Augmented reality support for assembly and maintenance tasks, reducing errors and training time
- 3D printing integration for rapid prototyping and custom manufacturing
- Energy management and sustainability tracking in production processes
- AI-driven product design optimization and lifecycle management
- Blockchain integration for secure and transparent supply chain collaboration in manufacturing
Business Intelligence and Analytics
BI modules have become more intuitive and predictive, offering actionable insights:
- AI-powered real-time dashboards and KPI tracking with anomaly detection
- Natural language querying for ad-hoc reporting and data exploration
- Predictive and prescriptive analytics with machine learning for scenario modeling
- Automated data discovery and insight generation with plain language narratives
- Advanced data visualization with augmented reality capabilities for immersive data exploration
- Edge computing integration for real-time analytics at the source of data generation
- AI-driven data governance and quality management
- Collaborative analytics features for team-based decision making
- Integration of external data sources for comprehensive market and competitive analysis
Project Management
Project management modules now offer more intelligent capabilities for efficient project delivery:
- AI-assisted project planning and resource allocation with optimized scheduling
- Predictive project risk assessment and mitigation strategies
- Real-time collaboration tools with virtual reality meeting spaces for remote teams
- Blockchain-enabled smart contracts for project agreements and milestone payments
- Sustainability impact tracking for projects with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) reporting
- AI-powered project portfolio management for strategic alignment
- Predictive analytics for project success probability and resource forecasting
- Agile and waterfall methodology support with AI-assisted methodology selection
Asset Management
Asset management modules have evolved to provide comprehensive lifecycle management:
- IoT integration for real-time asset tracking and performance monitoring
- Predictive maintenance scheduling using machine learning and historical data
- AI-driven asset lifecycle optimization and replacement planning
- Augmented reality for asset identification and maintenance guidance
- Blockchain integration for secure asset ownership and transfer records
- Energy efficiency tracking and optimization for physical assets
- Automated compliance management for asset-related regulations
- AI-powered asset utilization analysis and optimization recommendations
- Integration with financial modules for accurate depreciation and valuation
As we move into examining specific ERP system examples in the next section, we'll see how different vendors implement and emphasize these modules to cater to various industry needs and business sizes in 2025. Understanding these core modules will help in evaluating which ERP solutions best align with an organization's specific requirements and growth plans in the current technological landscape.
The integration of these advanced modules within modern ERP systems provides organizations with unprecedented capabilities to streamline operations, gain real-time insights, and make data-driven decisions. As technology continues to evolve, these modules will likely become even more sophisticated, incorporating emerging technologies like quantum computing and advanced AI to further enhance business processes and decision-making capabilities.
Top ERP System Examples for Different Business Sizes
In 2025, the ERP market offers a diverse range of solutions tailored to different business sizes and needs. Let's explore some of the top ERP system examples for small, mid-sized, and enterprise-level businesses, highlighting their key features, pricing models, and target markets:
ERP Solutions for Small Businesses
Small businesses require cost-effective, easy-to-implement ERP solutions that can scale with their growth. Two notable examples include:
1. Odoo
Odoo ERP is an open-source ERP with a modular approach, allowing businesses to start small and add functionality as needed.
- Cloud-based with optional on-premise deployment for flexibility
- Wide range of apps covering all core ERP functions, from CRM to manufacturing
- AI-powered business intelligence and automation features
- Low-code customization capabilities for easy adaptation to specific business needs
- Strong community support and extensive app marketplace
- Integrated e-commerce platform with omnichannel capabilities
- Odoo ERP Pricing: Starts at $24/user/month for the cloud version, with a free Community Edition available
2. Acumatica
Acumatica is a cloud-native ERP with industry-specific editions (e.g., manufacturing, construction, retail-commerce).
- Mobile-first design for accessibility across devices
- Flexible pricing based on transaction volume, not user count, beneficial for growing businesses
- Built-in AI and machine learning capabilities for process automation and insights
- Strong integration capabilities with third-party applications
- Advanced financial management with multi-entity and multi-currency support
- Robust project accounting and job costing features
ERP Solutions for Mid-sized Businesses
Mid-sized businesses often seek more robust features and scalability to support their growth. Two popular options in this category are:
1. Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central is a cloud-based ERP with strong integration with other Microsoft products (Office 365, Power BI).
- AI-powered insights and analytics leveraging Microsoft's advanced AI capabilities
- Mixed reality integration with Microsoft HoloLens for hands-free operations
- Extensible through AppSource marketplace for industry-specific solutions
- Advanced security features with Azure Active Directory integration
- Comprehensive financial management with AI-assisted cash flow forecasting
- Integrated CRM functionality with AI-driven sales insights
2. Oracle NetSuite
Oracle NetSuite is a cloud-native ERP suitable for fast-growing mid-sized companies with global aspirations.
- Unified suite including ERP, CRM, and e-commerce capabilities
- AI-driven business insights and process automation across all modules
- Global business management features for multi-subsidiary operations
- SuiteSuccess methodology for rapid implementation based on industry best practices
- Advanced revenue recognition and billing solutions
- Robust supply chain and inventory management capabilities
Enterprise-level ERP Solutions
Large enterprises require highly scalable, feature-rich ERP systems capable of managing complex global operations. Two leading examples are:
1. SAP S/4HANA Cloud
SAP S/4HANA Cloud is a next-generation ERP leveraging in-memory computing for real-time analytics and transactions.
- Comprehensive suite covering all business processes with industry-specific solutions
- Advanced AI and machine learning capabilities, including predictive analytics and intelligent automation
- Integration with SAP's intelligent technologies (IoT, blockchain, machine learning)
- Extensive ecosystem of partners and third-party applications
- Powerful financial consolidation and reporting tools for complex global operations
- Advanced supply chain management with real-time visibility and AI-driven optimization
2. Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP
Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP is a comprehensive cloud-based ERP suite designed for large, complex organizations.
- AI-powered financial management with continuous close capabilities
- Advanced supply chain planning and intelligent procurement
- Integrated enterprise performance management (EPM) for strategic planning
- Robust project management and execution capabilities
- AI-driven risk management and compliance features
- Extensive analytics and reporting capabilities with embedded AI
My Key Considerations When Choosing an ERP System in 2025
When evaluating these ERP examples, businesses should consider:
-
AI and automation capabilities: Look for systems with advanced AI features that can drive efficiency and provide actionable insights.
-
Industry-specific functionality: Choose solutions tailored to your sector, especially for regulated industries or those with unique processes.
-
Integration ecosystem: Evaluate the availability of pre-built integrations and APIs for connecting with other business systems and emerging technologies.
-
Scalability and flexibility: Ensure the system can adapt to your business growth and changing market conditions without requiring a complete overhaul.
-
User experience: Prioritize systems with intuitive interfaces and mobile capabilities to encourage adoption and maximize productivity.
-
Security and compliance: Assess the ERP's security features and compliance certifications, especially for cloud-based solutions handling sensitive data.
-
Total cost of ownership: Consider not just the initial price, but ongoing costs for maintenance, upgrades, and potential customizations.
-
Vendor innovation track record: Evaluate the vendor's history of incorporating emerging technologies and adapting to market trends.
-
Implementation and support: Consider the availability of implementation partners, training resources, and ongoing support options.
-
Cloud strategy: Determine whether a cloud, on-premise, or hybrid solution best fits your organization's IT strategy and data governance requirements.
By understanding these ERP system examples and their target markets, businesses can better align their choice with their specific needs, growth plans, and operational complexities in 2025 and beyond. It's important to note that the ERP market is continually evolving, with vendors regularly updating their offerings and new players emerging with innovative solutions.
When selecting an ERP system, organizations should conduct thorough research, engage in product demonstrations, and possibly undertake pilot projects to ensure the chosen solution aligns with their unique requirements. Additionally, considering the long-term partnership aspect of ERP implementation, factors such as vendor financial stability, product roadmap, and customer support quality should also play a role in the decision-making process.
In the next section, we'll explore industry-specific ERP solutions, further illustrating how these systems address unique sectoral requirements in the current technological landscape.
Industry-specific ERP System Examples
In 2025, industry-specific ERP solutions have become increasingly sophisticated, leveraging advanced technologies to address the unique challenges and requirements of particular sectors. These specialized systems offer out-of-the-box functionality tailored to industry-specific processes, regulations, and best practices. Let's explore some notable examples across various industries:
Manufacturing ERP
Manufacturing ERPs, also called Discrete ERPs, have evolved to embrace Industry 4.0 technologies, offering advanced capabilities for smart manufacturing:
1. Plex Smart Manufacturing Platform
Plex Smart Manufacturing Platform is a cloud-based ERP with real-time production monitoring and control.
- IoT integration for equipment performance tracking and predictive maintenance
- AI-powered quality management with machine vision integration
- Blockchain-enabled supply chain traceability for enhanced transparency
- Augmented reality support for assembly and maintenance procedures
- Advanced inventory management with AI-driven demand forecasting
- Energy management and sustainability tracking in production processes
2. IQMS Manufacturing ERP
IQMS Manufacturing ERP specializes in plastic manufacturing and related industries.
- Real-time machine monitoring with AI-driven optimization for improved OEE
- Advanced scheduling with machine learning algorithms for optimal production planning
- Integrated quality control with statistical process control (SPC) capabilities
- 3D printing integration for rapid prototyping and custom manufacturing
- Comprehensive supply chain management with supplier quality tracking
- Regulatory compliance management for industries like medical devices and automotive
Healthcare ERP
Healthcare organizations benefit from ERPs that address patient care, compliance, and resource management:
1. Infor CloudSuite Healthcare
Infor CloudSuite Healthcare is an AI-powered clinical and financial decision support for improved patient outcomes.
- Integrated electronic health record (EHR) system with interoperability features
- Predictive analytics for patient outcomes and resource allocation optimization
- Compliance management with automatic regulatory updates (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR)
- Telehealth integration and patient engagement tools for remote care management
- Supply chain optimization for medical supplies with expiration date tracking
- Workforce management tailored for healthcare shift scheduling and credentialing
2. Oracle Health
Oracle Health is a comprehensive healthcare management platform with advanced analytics.
- AI-driven clinical documentation and coding for improved accuracy and efficiency
- Population health management with social determinants of health integration
- Supply chain optimization for medical supplies with blockchain-enabled tracking
- Blockchain-enabled secure health information exchange for interoperability
- Revenue cycle management with AI-powered claims processing and denial prevention
- Patient experience management with personalized engagement tools
Retail and E-commerce ERP
Retail-focused ERPs now offer omnichannel capabilities and advanced customer insights:
1. Brightpearl
Brightpearl is an ERP that is tailored for omnichannel retailers and wholesalers with integrated POS systems.
- AI-powered demand forecasting and inventory optimization across channels
- Real-time order management across multiple sales channels and marketplaces
- Automated fulfillment with robotics integration for warehouse management
- Advanced customer segmentation and personalization using machine learning
- Integrated accounting and financial management for retail operations
- Dropshipping and multi-location inventory management capabilities
2. Manhattan Active Omni
Manhattan Active Omni is a cloud-native platform for unified commerce across digital and physical channels.
- AI-driven order orchestration and allocation for optimal fulfillment
- Real-time inventory visibility across the supply chain with RFID integration
- Personalized customer engagement with machine learning for next-best-action recommendations
- Augmented reality for virtual product try-ons and store navigation
- Advanced returns management with fraud detection capabilities
- Integrated customer service tools with AI-powered chatbots
Construction ERP
Construction ERPs have embraced mobile technology and advanced project management:
1. Procore
Procore is a cloud-based construction management platform with a mobile-first design.
- AI-powered risk assessment and mitigation for project planning
- IoT integration for equipment tracking and utilization optimization
- Drone and 3D modeling integration for project monitoring and progress tracking
- BIM (Building Information Modeling) integration for improved collaboration
- Advanced financial management with job costing and progress billing
- Safety management tools with AI-assisted hazard identification
- Procore Pricing: Based on project volume, starting from $375/month for small contractors
2. CMiC
CMiC is a unified platform for construction financials and operations.
- AI-assisted project planning and resource allocation optimization
- Predictive analytics for project performance and risk management
- Blockchain-enabled smart contracts for subcontractor management
- Augmented reality for blueprint visualization and on-site issue resolution
- Integrated document management with version control and approval workflows
- Advanced payroll management with multi-union and prevailing wage support
- CMiC Pricing: Custom quotes based on company size and project volume
Benefits of Industry-Specific ERP Solutions in 2025
Adopting an industry-specific ERP offers several advantages:
-
Tailored functionality: Out-of-the-box features designed for specific industry processes and workflows, reducing the need for extensive customization.
-
Faster implementation: Pre-configured industry best practices reduce customization needs and deployment time, accelerating time-to-value.
-
Regulatory compliance: Built-in features to meet industry-specific regulations, with automatic updates to keep pace with changing requirements.
-
Specialized analytics: Industry-specific KPIs and AI-powered insights for better decision-making aligned with sector-specific challenges.
-
Ecosystem integration: Pre-built connectors to industry-specific tools and platforms, facilitating a more comprehensive and integrated technology stack.
-
Future-proofing: Continuous updates aligned with industry trends and technological advancements, ensuring the system remains relevant.
-
Industry expertise: Vendors of industry-specific ERPs often have deep domain knowledge, providing valuable insights and best practices.
- Competitive advantage: Access to cutting-edge features tailored to industry needs can provide a significant edge over competitors using generic solutions.
Considerations When Choosing an Industry-Specific ERP
When evaluating these specialized solutions, consider:
- The vendor's expertise and track record in your specific industry, including case studies and references from similar organizations.
- The balance between industry-specific features and general ERP functionality to ensure all business needs are met.
- Integration capabilities with other industry-specific software you may use, such as CAD systems for manufacturing or EMR systems for healthcare.
- The system's ability to adapt to evolving industry trends and regulations, including the vendor's commitment to ongoing research and development.
- Support for emerging technologies relevant to your industry (e.g., IoT, blockchain, AR/VR) and the vendor's roadmap for incorporating these technologies.
- Scalability to support your business growth within the industry, including the ability to handle increased transaction volumes and user counts.
- The availability of industry-specific implementation partners and consultants who understand your sector's unique challenges.
- The total cost of ownership, including industry-specific customizations and ongoing maintenance of specialized features.
By understanding these industry-specific ERP examples and their unique value propositions, businesses can make more informed decisions when selecting a system that aligns closely with their sector's requirements in 2025 and beyond. These specialized solutions offer the potential for significant improvements in operational efficiency, compliance management, and competitive positioning within their respective industries.
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect industry-specific ERP solutions to become even more sophisticated, incorporating advanced AI, IoT, and other emerging technologies to address sector-specific challenges. Organizations should stay informed about these developments and regularly assess their ERP capabilities to ensure they are leveraging the most effective tools for their industry.
Benefits of Implementing an ERP System
Implementing an ERP system in 2025 offers transformative benefits that can significantly impact an organization's efficiency, competitiveness, and growth potential. Let's explore the key advantages:
Enhanced Business Process Efficiency
Modern ERP systems streamline operations by:
- Eliminating data silos and reducing manual data entry through AI-powered automation, minimizing errors, and improving data accuracy
- Standardizing processes across departments for consistency and efficiency, ensuring best practices are followed throughout the organization
- Enabling real-time collaboration between teams, regardless of location, fostering better communication and decision-making
- Automating complex workflows with machine learning algorithms, freeing up employees to focus on higher-value tasks
- Providing a single source of truth for all business data, eliminating discrepancies, and improving data integrity
For example, a manufacturing company using Plex Smart Manufacturing Platform could see a 30% increase in production efficiency by integrating IoT sensors with AI-driven production scheduling, optimizing resource utilization and reducing downtime.
Data-Driven Decision Making
ERP systems empower organizations to make informed decisions through:
- Real-time, accurate data from across the organization, providing a comprehensive view of business operations
- AI-powered predictive analytics for forecasting and risk management, enabling proactive decision-making
- Customized dashboards with natural language querying capabilities, making data accessible to non-technical users
- Automated insight generation and anomaly detection, highlighting areas that require attention
- Advanced scenario modeling and simulation tools for strategic planning
A retail business using Manhattan Active Omni, for instance, could leverage its AI-driven demand forecasting to reduce inventory costs by 20% while improving product availability, optimizing working capital and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Improved Customer Experience
Modern ERP systems enhance customer satisfaction by:
- Providing a 360-degree view of customer interactions across all touchpoints, enabling personalized service
- Enabling faster response times through AI-powered chatbots and automated workflows, improving customer support efficiency
- Personalizing marketing and sales efforts based on comprehensive customer data and AI insights, increasing conversion rates
- Ensuring more accurate order fulfillment and delivery through integrated supply chain management, reducing errors and delays
- Offering self-service portals and mobile apps for customers to access information and place orders, enhancing convenience
A healthcare provider using Oracle Health could improve patient outcomes by 15% through personalized care plans based on AI-analyzed patient data and population health trends, leading to higher patient satisfaction and better health outcomes.
Enhanced Scalability and Flexibility
Modern ERP systems, especially cloud-based solutions, offer:
- The ability to easily add users and functionality as the business grows, without significant infrastructure investments
- Support for multi-site and multi-country operations with localization features, facilitating global expansion
- Flexibility to adapt to changing business models and market conditions, ensuring long-term viability
- Easy integration of emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain, future-proofing the organization
- Modular architecture allows businesses to start with core functionalities and add modules as needed
A fast-growing e-commerce business using Brightpearl could quickly expand into new markets and sales channels without significant IT infrastructure investments, scaling operations seamlessly to meet increasing demand.
Improved Compliance and Risk Management
ERP systems enhance regulatory compliance and risk mitigation through:
- Built-in controls and audit trails for financial compliance, reducing the risk of fraud and errors
- Enhanced data security with AI-powered threat detection, protecting sensitive business and customer information
- Automated updates to keep pace with changing regulations, ensuring continuous compliance
- Improved visibility for identifying and mitigating potential risks across the organization
- Centralized data management facilitating easier audits and regulatory reporting
A construction company using Procore could reduce compliance-related risks by 40% through automated documentation and AI-assisted risk assessment, ensuring adherence to safety regulations and contract requirements.
Cost Savings and ROI
While the initial investment in an ERP system can be significant, the long-term benefits often lead to substantial cost savings:
- Reduced IT costs through the consolidation of multiple systems into a single, integrated platform
- Lower inventory costs through AI-driven forecasting and management, optimizing stock levels
- Increased productivity and reduced labor costs through automation of routine tasks
- Improved financial management and cash flow optimization, enhancing overall financial performance
- Reduced operational costs through process optimization and elimination of inefficiencies
A study by Nucleus Research found that ERP implementations in 2025 deliver an average ROI of 7.23 for every dollar spent, with cloud-based systems showing even higher returns due to lower upfront costs and faster implementation times.
Competitive Advantage
By integrating all the benefits discussed above, ERP systems ultimately provide organizations with a significant competitive edge:
- Faster time-to-market for new products and services, enabling businesses to capitalize on emerging opportunities
- Improved agility to respond to market changes and customer demands, staying ahead of competitors
- Enhanced ability to leverage data for innovation and strategic planning, driving business growth
- Better positioning for digital transformation initiatives, ensuring the organization remains technologically advanced
- Improved collaboration with suppliers and partners, creating more efficient and responsive supply chains
For example, a manufacturer using SAP S/4HANA Cloud could reduce product development cycles by 30% through integrated product lifecycle management and AI-assisted design processes, bringing innovative products to market faster than competitors.
Sustainability and ESG Compliance
Modern ERP systems are increasingly supporting sustainability initiatives:
- Carbon footprint tracking and reporting across the supply chain, supporting environmental goals
- Energy consumption monitoring and optimization, reducing costs and environmental impact
- Waste reduction through improved resource planning and circular economy initiatives
- Support for sustainable sourcing and supplier evaluation based on ESG criteria
- Automated ESG reporting and compliance management, meeting stakeholder expectations
A company using Infor CloudSuite, for instance, could improve its ESG ratings by leveraging built-in sustainability tracking and reporting features, potentially attracting environmentally conscious customers and investors, and ensuring compliance with emerging sustainability regulations.
As we've seen throughout this guide, the benefits of ERP systems in 2025 are far-reaching and can transform every aspect of an organization's operations. From enhancing efficiency and decision-making to driving innovation and sustainability, ERP systems have become indispensable tools for businesses looking to thrive in an increasingly complex and competitive global marketplace.
Organizations implementing ERP systems should approach the process strategically, aligning the implementation with their business goals and carefully managing the change process to maximize the realization of these benefits. Regular assessment and optimization of the ERP system post-implementation can ensure that the organization continues to derive value from its investment, adapting to new challenges and opportunities as they arise.
Challenges and Considerations When Choosing an ERP System
While the benefits of implementing an ERP system are substantial, organizations must navigate several challenges and carefully consider various factors to ensure a successful ERP adoption in 2025. Let's explore key considerations and potential pitfalls in the ERP selection and implementation process:
Aligning ERP with Business Strategy
One of the most critical challenges is ensuring that the chosen ERP system aligns with the organization's long-term business strategy. Consider:
- How the ERP will support your company's growth plans and digital transformation initiatives
- The system's ability to adapt to potential pivots in your business model or market conditions
- Compatibility with your organization's culture and ways of working
- The ERP's capacity to integrate emerging technologies relevant to your industry
- Alignment with your company's global expansion plans, if applicable
For example, a manufacturing company planning to expand internationally should prioritize ERP systems with robust multi-currency, multi-language, and localization capabilities to support global operations.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
While we've discussed cost savings, it's crucial to consider the full TCO of an ERP system, including:
- Initial licensing or subscription costs
- Implementation and customization expenses
- Training and change management costs
- Ongoing maintenance and support fees
- Potential hardware upgrades or cloud infrastructure costs
- Costs associated with integrating emerging technologies (AI, IoT, etc.)
- Data migration and cleansing expenses
- Opportunity costs during implementation and potential productivity dips
Organizations should conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis, considering both short-term expenses and long-term ROI. Cloud-based solutions often offer lower upfront costs but may have higher ongoing subscription fees. It's essential to project costs over a 5-10 year period to get a true picture of TCO.
Data Migration and Integration
Data integration remains a significant challenge, even with advanced technologies:
- Ensuring data quality and consistency when migrating from legacy systems
- Integrating the ERP with existing specialized software and emerging technologies
- Managing data security and compliance during the migration process
- Handling real-time data synchronization across multiple systems
- Addressing data governance and ownership issues across departments
Careful planning and potentially engaging data migration specialists can help mitigate these risks. Look for ERPs with robust API libraries and pre-built connectors to ease integration challenges. Consider implementing a data governance framework to ensure ongoing data quality and consistency.
Customization vs. Configuration
Organizations often face the dilemma of whether to customize a general ERP or configure an industry-specific solution:
- Customization can provide a perfect fit but may increase costs and complexity
- Configuration of pre-built modules is often faster and more cost-effective but may require some process changes
- Over-customization can make future upgrades more difficult and expensive
- Industry-specific solutions may offer a better fit out-of-the-box but could limit flexibility
The key is finding the right balance that meets your unique needs without overcomplicating the system. Look for ERPs with low-code/no-code customization tools to reduce dependency on IT for minor adjustments. Consider adopting industry best practices where possible to minimize the need for customization.
User Adoption and Change Management
Even the most advanced ERP system will fail if employees don't use it effectively. Key considerations include:
- Developing a comprehensive change management strategy
- Providing thorough training tailored to different user groups and roles
- Ensuring leadership buy-in and visible support for the ERP initiative
- Addressing potential resistance to change proactively
- Leveraging AI-powered user assistance and contextual learning tools
- Implementing a continuous improvement process to address user feedback
Engaging employees early in the process and demonstrating the personal benefits of the new system can significantly improve adoption rates. Consider ERPs with intuitive user interfaces and mobile capabilities to enhance user experience. Implement a robust internal communication plan to keep all stakeholders informed throughout the implementation process.
Scalability and Future-Proofing
As technology continues to evolve rapidly, it's crucial to choose an ERP that can adapt to future needs:
- Assess the ERP vendor's track record of innovation and keeping pace with technological advancements
- Evaluate the system's ability to integrate with emerging technologies like AI, IoT, blockchain, and quantum computing
- Consider the flexibility to add or remove modules as your business needs evolve
- Look for ERPs with open architectures that allow for easy integration of future technologies
- Assess the vendor's commitment to ongoing research and development
Choosing a forward-looking ERP partner can help ensure your system remains relevant and effective for years to come. Consider the vendor's roadmap and how it aligns with your organization's future plans and industry trends.
Implementation Timeline and Resource Allocation
ERP implementations can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Organizations must carefully consider:
- Realistic timelines for each phase of the implementation
- The internal resources required and their availability
- The potential impact on day-to-day operations during implementation
- Whether a phased rollout or a "big bang" approach is more appropriate
- The need for external consultants or implementation partners
- Contingency plans for potential delays or issues
Proper project management and clear communication are essential for keeping the implementation on track. Look for ERPs with rapid implementation methodologies and industry-specific templates to accelerate deployment. Consider forming a dedicated implementation team with representatives from all key departments.
Vendor Evaluation and Partnership
Beyond features and capabilities, it's crucial to evaluate potential ERP vendors as long-term partners:
- Assess their financial stability and long-term viability
- Evaluate their customer support and service level agreements
- Consider their ecosystem of implementation partners and third-party add-ons
- Review case studies and speak with reference customers in your industry
- Assess their commitment to ongoing innovation and technology integration
- Evaluate their global presence and ability to support international operations
Remember, implementing an ERP is the beginning of a long-term relationship with the vendor, not just a one-time purchase. Choose a vendor that aligns with your organization's values and long-term vision.
Security and Compliance
With increasing cyber threats and regulatory requirements, security and compliance are paramount:
- Evaluate the ERP's built-in security features and compliance certifications
- Assess the vendor's track record in addressing security vulnerabilities
- Consider data residency requirements, especially for cloud-based solutions
- Look for ERPs with AI-powered security features for proactive threat detection
- Ensure the system can meet industry-specific regulatory requirements
- Assess the vendor's data privacy practices and compliance with regulations like GDPR
Ensure that the chosen ERP can meet your industry's specific regulatory requirements and adapt to evolving compliance landscapes. Consider engaging cybersecurity experts to assess the ERP's security capabilities.
Conclusion
By carefully considering these challenges and factors, organizations can significantly increase their chances of a successful ERP implementation in 2025. While the process may seem daunting, the potential benefits in terms of efficiency, insight, and competitive advantage make it a worthwhile endeavor for businesses of all sizes and industries.
As we conclude our comprehensive guide to ERP system examples, it's clear that the right ERP solution can be transformative for an organization. By understanding the various types of systems available, their core modules, industry-specific offerings, and the challenges involved in selection and implementation, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals and set them up for long-term success in an increasingly digital business landscape.
Remember that ERP implementation is a journey, not a destination. Continuous evaluation, optimization, and adaptation of your ERP system will be necessary to ensure it continues to meet your organization's evolving needs and leverages the latest technological advancements. With careful planning, strong leadership commitment, and a focus on change management, organizations can overcome the challenges of ERP implementation and reap the substantial benefits these systems offer in the dynamic business environment of 2025 and beyond.
Future Trends in ERP Systems
As we look ahead, the ERP landscape continues to evolve rapidly, building upon the foundational elements and benefits we've explored in previous sections. Let's examine some of the key trends shaping the future of ERP systems beyond 2025:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
AI and ML will become even more deeply integrated into ERP systems:
- Autonomous ERP systems that can self-optimize and self-heal, reducing the need for manual interventions
- Advanced natural language processing for conversational interfaces and voice-activated ERP interactions, improving user experience and accessibility
- Predictive analytics evolving into prescriptive analytics, offering actionable recommendations for complex business decisions
- AI-driven process mining for continuous improvement of business processes, automatically identifying inefficiencies and suggesting optimizations
- Cognitive automation for handling complex, judgment-based tasks, freeing up human resources for more strategic activities
- Personalized AI assistants for each user role, providing context-aware support and insights
For instance, future ERPs might use AI to automatically adjust global supply chain strategies based on real-time geopolitical events, market data, and environmental factors, ensuring resilience and efficiency.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Edge Computing
IoT integration will extend beyond current capabilities:
- Seamless integration of IoT data from across the entire value chain, providing unprecedented visibility into operations
- Edge computing for real-time processing of IoT data, reducing latency and bandwidth usage while enabling faster decision-making
- Digital twins for virtual modeling and simulation of physical assets and processes, allowing for predictive maintenance and optimization
- Predictive maintenance evolving into prescriptive maintenance, autonomously scheduling and performing maintenance tasks
- Advanced sensor networks for real-time environmental monitoring and sustainability tracking
- Integration of augmented reality devices with IoT data for enhanced field service and remote assistance
This enhanced connectivity will enable truly smart factories and supply chains, with ERPs serving as the central nervous system for these interconnected ecosystems, optimizing operations in real-time based on a constant stream of data.
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technologies
Blockchain integration in ERPs will mature as the technology improves, offering:
- Enhanced security and transparency in multi-party transactions, reducing fraud and improving trust
- Immutable audit trails for regulatory compliance, simplifying audits and reducing compliance costs
- Smart contracts for automated, secure business processes across organizational boundaries, streamlining complex multi-party workflows
- Decentralized identity management for improved data protection and privacy, giving users more control over their personal information
- Tokenization of assets for more efficient and transparent supply chain finance, improving liquidity for suppliers
- Blockchain-based loyalty programs and customer engagement initiatives, creating new opportunities for customer retention
These features could revolutionize how ERPs handle inter-company transactions, supply chain management, and regulatory compliance, creating more transparent and efficient business ecosystems.
Quantum Computing Integration
As quantum computing matures, it will begin to impact ERP systems:
- Quantum-enhanced optimization for complex supply chain and logistics problems, solving previously intractable issues
- Advanced cryptography for ultra-secure data protection, safeguarding against future cybersecurity threats
- Quantum machine learning algorithms for processing vast amounts of data, uncovering deeper insights
- Simulation of molecular and material properties for R&D in manufacturing and pharmaceutical ERPs, accelerating product development
- Financial modeling and risk analysis at unprecedented scales, improving decision-making in volatile markets
- Quantum-inspired algorithms for classical computers, bringing some benefits of quantum computing to traditional hardware
While still in its early stages, quantum computing could provide a significant leap in processing power for specific ERP functions, potentially revolutionizing areas like supply chain optimization, financial modeling, and advanced analytics.
Augmented and Virtual Reality Integration
AR and VR will become more prevalent in ERP interfaces:
- Immersive data visualization for complex analytics and decision-making, allowing users to "walk through" their data
- AR-assisted inventory management and warehouse operations, improving accuracy and efficiency
- Virtual training environments for employee onboarding and skill development, reducing training costs and improving outcomes
- Remote assistance and collaboration tools for field service and maintenance, enabling expert support from anywhere
- Virtual product design and prototyping integrated with ERP data, accelerating the product development cycle
- AR-enhanced quality control processes, improving defect detection and reducing errors
These technologies will enhance user interaction with ERP systems, making complex data more accessible and actionable, while also improving operational processes in areas like manufacturing, maintenance, and training.
Hyper-Personalization and Contextual ERPs
ERPs will become more adaptive to individual users and contexts:
- AI-driven interfaces that adapt to each user's role, preferences, and work patterns, improving productivity and user satisfaction
- Contextual insights and recommendations based on real-time situational awareness, providing relevant information at the right time
- Predictive user interfaces that anticipate user needs and actions, streamlining workflows
- Integration with personal productivity tools for seamless workflow management across platforms
- Emotion AI integration to understand and respond to user sentiment, improving user experience and support
- Personalized learning and development paths integrated with ERP usage data, facilitating continuous skill improvement
This level of personalization will significantly enhance user adoption and productivity, making ERP systems more intuitive and valuable for individual users.
Sustainability and Circular Economy Support
ERPs will play a crucial role in supporting sustainability initiatives:
- Advanced carbon footprint tracking and reporting across the entire value chain, supporting environmental goals and regulatory compliance
- Circular economy modules for managing product lifecycles, recycling, and reuse, promoting sustainable business practices
- AI-driven sustainability optimization for resource allocation and process efficiency, reducing waste and energy consumption
- Integration with external sustainability data sources for comprehensive ESG reporting, improving transparency for stakeholders
- Predictive modeling for environmental impact assessment of business decisions, supporting sustainable strategy development
- Blockchain-enabled tracking of sustainable sourcing and ethical supply chains, ensuring compliance and building consumer trust
These features will help organizations meet increasingly stringent sustainability regulations and stakeholder expectations, while also identifying opportunities for cost savings and innovation through sustainable practices.
Intelligent ERP (i-ERP) Ecosystems
The convergence of these trends is leading to the concept of Intelligent ERP ecosystems:
- Self-learning systems that continuously optimize business processes across organizational boundaries, adapting to changing conditions
- Autonomous decision-making capabilities for routine and complex scenarios, reducing the need for human intervention in day-to-day operations
- Seamless integration with external data sources and AI services for enhanced insights, providing a more comprehensive view of the business environment
- Collaborative networks of intelligent ERPs sharing anonymized data for industry-wide optimization, creating new benchmarks and best practices
- Predictive and prescriptive analytics that span entire value chains, optimizing performance across multiple organizations
- AI-driven scenario planning and strategy development tools, supporting more agile and informed decision-making at the executive level
i-ERPs represent the next evolution in enterprise systems, promising to deliver even greater efficiency and competitive advantage by creating interconnected, intelligent business ecosystems.
Conclusion
As we've seen throughout this guide, ERP systems have come a long way from their origins in manufacturing and finance. The future trends we've explored here build upon the core functionalities, deployment models, and industry-specific solutions discussed earlier, promising even greater value for businesses willing to embrace these innovations.
However, as with any technological advancement, organizations must carefully consider how these trends align with their strategic goals and operational needs. The challenges of implementation, user adoption, and change management discussed in the previous section will remain relevant, perhaps even more so as ERPs become increasingly sophisticated.
By staying informed about these trends and working closely with ERP vendors and implementation partners, businesses can position themselves to leverage the full potential of next-generation ERP systems. This proactive approach will drive innovation, efficiency, and growth in an increasingly complex and competitive business landscape, ensuring organizations remain agile and resilient in the face of future challenges and opportunities.
As we look to the future of ERP systems, it's clear that the line between different enterprise technologies will continue to blur. ERPs will increasingly serve as the central platform for digital transformation initiatives, integrating with and orchestrating a wide range of technologies to create truly intelligent enterprises. Organizations that successfully leverage these advanced ERP capabilities will be well-positioned to thrive in the dynamic and technology-driven business environment of the future.
Additional ERP System Resources
For more information on ERP systems and their implementation, consider exploring the following resources:
These resources provide additional insights, user reviews, and comparisons of various ERP systems, helping you make an informed decision for your organization's specific needs.
 by Evan Sherbert / February 3, 2025
by Evan Sherbert / February 3, 2025![G2CM_FI551_Learn_Article_Images_[10_Best_Free_CRM_Software]_V1a G2CM_FI551_Learn_Article_Images_[10_Best_Free_CRM_Software]_V1a](https://learn.g2.com/hs-fs/hubfs/G2CM_FI551_Learn_Article_Images_%5B10_Best_Free_CRM_Software%5D_V1a.png?width=690&name=G2CM_FI551_Learn_Article_Images_%5B10_Best_Free_CRM_Software%5D_V1a.png)
![]()
 by Sudipto Paul
by Sudipto Paul
 by Sudipto Paul
by Sudipto Paul
 by Mara Calvello
by Mara Calvello
 by Sudipto Paul
by Sudipto Paul
 by Sudipto Paul
by Sudipto Paul


