Picture a world where digital and physical realities coexist seamlessly. You glance around your office, and 3D product prototypes appear right on your desk. A remote teammate joins you as a life-sized hologram, adjusting designs in real time. Or you step into a virtual showroom that mirrors your physical surroundings — blending presence, data, and interaction into one unified experience.
What is mixed reality?
Mixed reality (MR) is a blend of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) that allows digital objects to interact with the physical world in real-time. It bridges the gap between on-screen and real-life experiences, letting users collaborate, communicate, and explore 3D environments from anywhere.
Mixed reality is powered by augmented reality visualization software — tools that merge spatial computing, 3D rendering, and real-time interaction to create immersive experiences. These platforms help businesses visualize products, design spaces, and deliver interactive demos through headsets, mobile devices, or web-based interfaces.
By blending the familiarity of the physical world with digital creativity, MR has become a powerful tool for marketing, product visualization, and immersive storytelling.
TL;DR: Everything you need to know about mixed reality
- What is mixed reality? It’s a blend of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) that enables digital objects to interact with the real world in real-time.
- How is MR different from AR and VR? AR adds digital elements to your surroundings, VR replaces them entirely, and MR merges both so virtual objects respond to physical environments.
- How does mixed reality work? uses AI-powered sensors, cameras, and spatial mapping to overlay lifelike 3D visuals that move, react, and adapt within your real space.
- Where is MR used today? In marketing (virtual product demos), education (interactive learning), healthcare (surgical simulations), construction (3D site mapping), and entertainment (immersive shows).
- What are the benefits of MR? It boosts engagement, improves training safety, enhances focus, personalizes experiences, and builds customer trust through lifelike interaction.
- What are the challenges of MR? High costs, complex setup, limited expertise, and slow adoption due to hardware demands and steep learning curves.
- Why does MR matter? It’s reshaping how we work, learn, and connect—blurring the line between imagination and reality to create immersive experiences that feel truly human.
Augmented reality vs. virtual reality vs. mixed reality
Augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR) are all part of the broader field known as extended reality (XR), a term encompassing technologies that blend or simulate real and digital environments. While each offers a different level of immersion, together they represent the foundation of today’s immersive tech ecosystem.
Augmented reality enhances the real world by overlaying digital elements, such as text, images, or animations, onto a user’s physical surroundings. It doesn’t replace reality; it enriches it. AR experiences rely on devices like smartphones, smart glasses, and AR headsets equipped with sensors and gyroscopes. Common examples include Pokémon Go and Snap AR, where users interact with virtual objects in real environments for entertainment, education, or engagement.
Virtual reality offers a fully immersive digital environment, replacing the physical world with a computer-generated one entirely. Users typically wear headsets that block out real-world surroundings, allowing them to explore virtual spaces designed for gaming, training, communication, or social interaction. As the technological backbone of the metaverse, VR enables shared digital experiences and remote collaboration across borders.

Mixed reality merges aspects of both AR and VR, enabling real-time interaction between digital and physical elements. In MR environments, virtual 3D objects not only appear in the user’s real space but also respond to it, recognizing surfaces, lighting, and even gestures. This makes it difficult at times to distinguish what’s real from what’s computer-generated. As MR technologies mature and become more accessible through cloud networks and wearable devices, they are poised to drive the next wave of immersive communication and collaboration.
How does mixed reality work?
Mixed reality works by combining real-world perception with computer-generated imagery to create interactive, three-dimensional experiences. It relies on a combination of hardware, software, and cloud computing to sense, process, and project digital content into physical spaces.
MR devices are equipped with AI-powered sensors, cameras, processors, and GPUs that capture the user’s environment and interpret spatial data in real time. This allows the system to accurately position digital objects within the user’s surroundings. The more advanced the hardware, the smoother and more lifelike the mixed reality experience becomes.
Common MR devices include smart glasses, motion-tracking gloves, body suits, smartphones, and headsets. These devices connect, either wirelessly or via cables, to computers or consoles running mixed reality software.
The software generates and manages digital content that interacts with the real world. It can add, move, or transform 3D objects so they appear to exist physically. Developers often use software development kits (SDKs) and spatial mapping frameworks to design these immersive environments.
Modern MR headsets, such as the HTC Vive and Meta Quest 3, use advanced optics and spatial mapping to create high-fidelity, responsive virtual environments. These systems detect movement, recognize gestures, and adapt to the user’s surroundings, seamlessly merging physical and digital interactions.
Accurate input sensing, which enables the system to detect motion, touch, and orientation, is crucial for effective operation. If this tracking fails, the user’s sense of immersion is disrupted. The complexity and precision of MR technology are what enable it to deliver a continuous, realistic, and interactive experience.
Here's a list of a few components a good MR solution needs to track for a perfect mixed reality experience.
- Detect physical objects via spatial mapping and bounding boxes
- Real environment perception to create computer-generated replicas
- Input devices like cameras, motion controllers, bodysuits, and treadmill floors
- Object recognition to detect and classify real-world objects and their categories
- Locations and position tracking in both physical and virtual environments to register relationships
- Ambisonics or virtual lights for added realism while displaying virtual content
- Collaboration on 3D assets in mixed reality spaces to enhance virtual look and feel
Top AR visualization tools in 2025
- Moderlry for real-time 3D product visualization and immersive space planning in retail and architecture.
- Within for interactive storytelling and experiential marketing through cinematic mixed reality campaigns.
- Overly for creating no-code AR experiences, product demos, and digital overlays across print and packaging.
- MirrAR for virtual try-ons in fashion and jewelry, combining lifelike rendering with e-commerce integration.
- CameraIQ for social AR effects and branded camera filters optimized for cross-platform marketing campaigns.
* These tools are top-rated in their category, according to G2's Fall 2025 Grid Reports.
What are the different types of mixed reality devices?
Mixed reality solutions typically use two main types of devices: holographic and immersive, each offering a different level of digital interaction and environmental blending.
- Holographic devices overlay interactive holograms onto the user’s real-world view, creating a semi-immersive experience. These devices enable users to view and interact with both physical and virtual elements simultaneously.
Examples include the Microsoft HoloLens, Magic Leap, and Lenovo ThinkReality A3. Holographic devices are widely used in manufacturing, healthcare, and engineering to provide remote assistance, 3D visualization, and hands-free guidance for tasks such as product assembly, equipment maintenance, and design prototyping.
- Immersive devices completely replace the user’s surroundings with a digital environment using head-mounted displays (HMDs). Each headset contains two near-eye screens, one for each eye, to create depth perception and a realistic sense of 3D presence. These devices also provide six degrees of freedom (6DoF), allowing users to move their head, arms, and body naturally in virtual space without breaking immersion.
Examples include Meta Quest 3, HTC Vive, and Apple Vision Pro. Immersive MR devices are commonly used for simulation-based training, design visualization, gaming, and virtual collaboration.
Together, these two types of devices form the foundation of mixed reality technology, merging physical awareness with digital interactivity to change how people work, learn, and communicate.
What are the use cases of mixed reality?
MR empowers you to connect with anyone, regardless of your location or whether a computer is available. As a recent innovation, organizations are still testing their use cases and applications for business operations.
Mixed reality in marketing
Startups from diverse segments are seeking to scale their returns on investment (ROIs) by transitioning into immersive technology. The recent growth of mixed reality has encouraged businesses to use it to expand their marketing campaigns.
Mixed reality has extensive use cases in product advertising and marketing, as it provides a hands-free product experience to customers. Using MR headsets, consumers can experiment with and interact virtually with a company’s products or services before making a purchase.
Mixed reality in education
There’s a big advantage to using mixed reality technology in schools and other educational applications, such as seminars or lectures.
Source: NTLTP
This video went viral when it was first released in 2016. The lifelike whale bursts through the gym floor. See how the water pools on the ground, just as it would in real life. That makes MR special: the digital object (water) interacting believably with the physical world (floor).
Mixed reality in training
Nearly every industry can adopt mixed reality into employee training and staff management processes. Companies like DHL, Xerox, and IBM empower their employees with MR/VR-based training and upskilling program simulations.
With mixed reality, employees can connect and collaborate with mentors in real-time to receive training, saving them valuable time. Driven by runtime AI, these interactions are platform-independent and let both the learner and trainer visualize and understand different processes that go into the training module.
Mixed reality in entertainment
The obvious shock factor of this type of technology can leave an audience in awe, but there are numerous aspects of events and entertainment that could benefit from MR technology.
Source: NewscastStudio
The Weather Channel has started to use mixed reality technology on its programs to give viewers a more realistic understanding of the current conditions and offer guidance on protecting themselves in case of dangerous weather.
MR is a new wave in technology, so its entertainment applications are a little unusual. For example, Angry Birds First Person Slingshot is an MR gaming experience that uses Magic Leap headsets to superimpose birds into your surroundings.
Mixed reality in healthcare
MR simulations create a hologram effect of real human body parts. Hovering a mobile device over a targeted area creates 3D interactive models of organs, allowing for a deeper understanding to their functioning. It has also become a powerful tool for training medical professionals, students, and remotely operating field medics. In radiology, surgeons can use MR-powered X-ray vision to see through a patient's skin and identify blood vessels and bones.
Mixed reality can be extremely effective to implement during critical surgeries, and can even save lives.
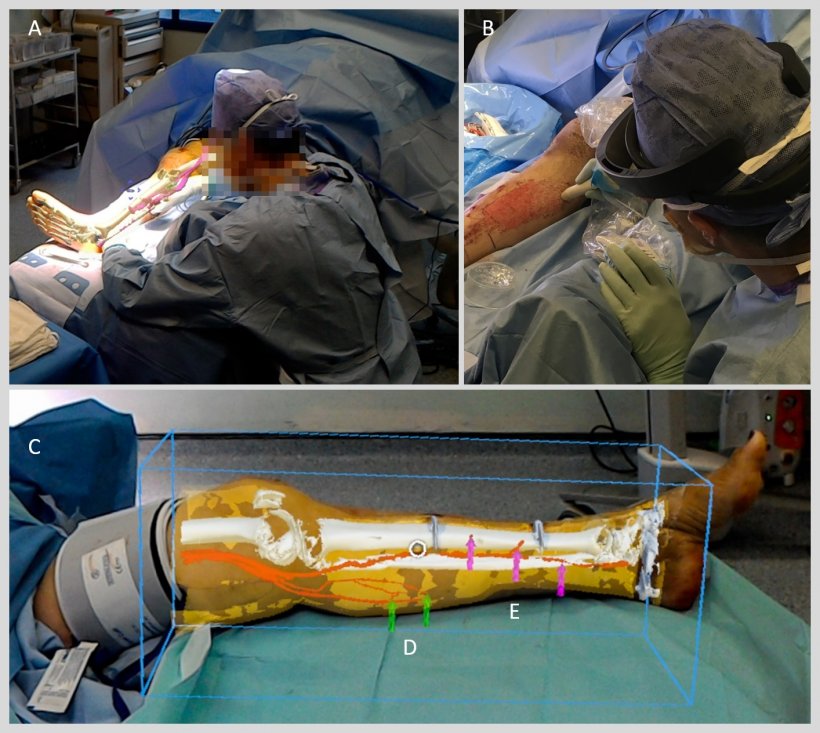
Source: healthcare-in-europe.com
Mixed reality in construction or engineering
MR devices can create virtual site maps for project engineers, architects, and onsite workers to use while working remotely. Coupled with BIM software, designers and architects illustrate their projects via mixed reality holograms.
You can use MR to conceptualize building structures in many forms without traveling long distances for site visits. Whether the pillar markings are off or the parapet is short, whether the paint doesn’t suit or the plywood needs to be changed, mixed reality gives an insight into everything.
Mixed reality in manufacturing
Mixed reality teleports production or manufacturing plants directly into your company’s space. You can oversee assembly lines, inventory, and supply levels from the comfort of your office. MR acts as a vehicle that lets you and your team monitor and test production processes without actually having to be in close proximity to it.The software device changes or highlights manufacturing issues or runs checks in real-time. Japan Airlines (JAL) actively uses Microsoft HoloLens to train engineers with virtual assistance from their location.
Mixed reality video calls
Video calls are a great way to communicate with someone who is not in the same room as you. Well, with MR, they actually can be with you (kind of). Mixed reality video conferencing allows you can move the ‘screen’ around and interact in new ways.
Source: Microsoft HoloLens
With this technology, the person on the other end of the call doesn’t need a headset to take part. They can even draw on their screens to convey what they are trying to say, which will place holograms over physical objects in your view.
Did you know? Microsoft Windows Mixed Reality Portal is a part of Windows 10 and 11. Through its flagship HoloLens, it provides unique access to live sports and entertainment and connects with others in the ultimate high-octane VR gaming experience.
Source: Microsoft
What are the benefits of mixed reality?
Advancements in immersive mixed reality technology have opened up new avenues for both commercial and non-commercial sectors. Ideas that were once envisioned in sci-fi movies have slowly and gradually become a reality.
Let’s discuss just a few of the benefits we get from MR.
- Strong customer base: Mixed reality combined with next-level AI can create unforgettable customer experiences at scale. Customers can experiment with something, try it on, or learn how to use it through instructional videos or virtual manuals in real life.
- Trustworthiness: Trusted brands like Facebook, Apple, and Samsung are already investing in subsidiaries that will develop MR experiences for the general public. These initiatives are also heavily funded in the investment world, which could reduce doubt in the minds of consumers.
- Increased concentration: MR combines natural and digital elements in unexpected ways that keep people focused until their experience is over.
- Hyper-personalization: No other form of media passes as more personal and engaging for customers than mixed reality. The individual immersed in a mixed reality scenario works with digital information more closely while in their physical world.
- Virtual demos for vendors: If you are a B2B company, you can provide holographic devices to your clients for virtual walkthroughs of the product, showcasing features, modules, applications, and results in the customer’s living space.
- Reduced mishaps: Utilizing MR technology as an adaptive training simulator for high-risk scenarios, such as mining, archaeology, or mountain climbing, reduces casualties and accidents.
- Conducive learning: Mixed reality's cousin, augmented reality, has successfully broken down the outdated barriers to education, providing an experiential environment for students to learn, brainstorm, and interact.
What are the challenges of mixed reality?
As mixed reality has been adopted only recently, companies are still investing money in deeper research to see how they can use it as a part of their business funnel.
Mixed reality is driven by immersive technology and artificial intelligence, two standalone digital technologies that haven’t been widely implemented on their own. MR requires exceptional talent, and the process of creating 3D content is expensive, time-consuming, and hardware-intensive. Let’s examine some of the challenges we face in standardizing mixed reality.
- Cost: The upfront cost of creating partially real and partially virtual environments is a lot. Aside from the hardware costs, investing in proper software development kits and hiring efficient developers who can curate customized applications costs thousands of dollars, with no guaranteed ROI.
- Old spatial mapping techniques: Based on computational geometry or other mathematical techniques, which give only an approximate estimate of the position or location of a real-world object. Deploying 3D elements in any given environment requires the precise mapping of real-world coordinates.
- Trained workforce: Service specialists, data analysts, and software engineers to build, train, and test the entire infrastructure from scratch are necessary if you want to create an optimal MR experience. It’s one of the major MR challenges faced by industries today.
- Time-consuming: MR is unlikely to be chosen as an efficient way of generating ROI. A startup’s minimum viable product (MVP) requires efficient marketing, followed by lightning-fast production, such as just-in-time, to spike sales. Mixed reality takes its own sweet time to show results.
- User experience: Across different parts come with different levels of tech savviness. Some might not be comfortable using a device to experience MR.
What’s new in mixed reality in 2025?
Mixed reality sits at the midpoint of this continuum, where elements of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) converge to create a seamless blend of both. Milgram and Kishino defined MR as an environment in which real and digital objects coexist and interact, with each element dynamically responding to the other.
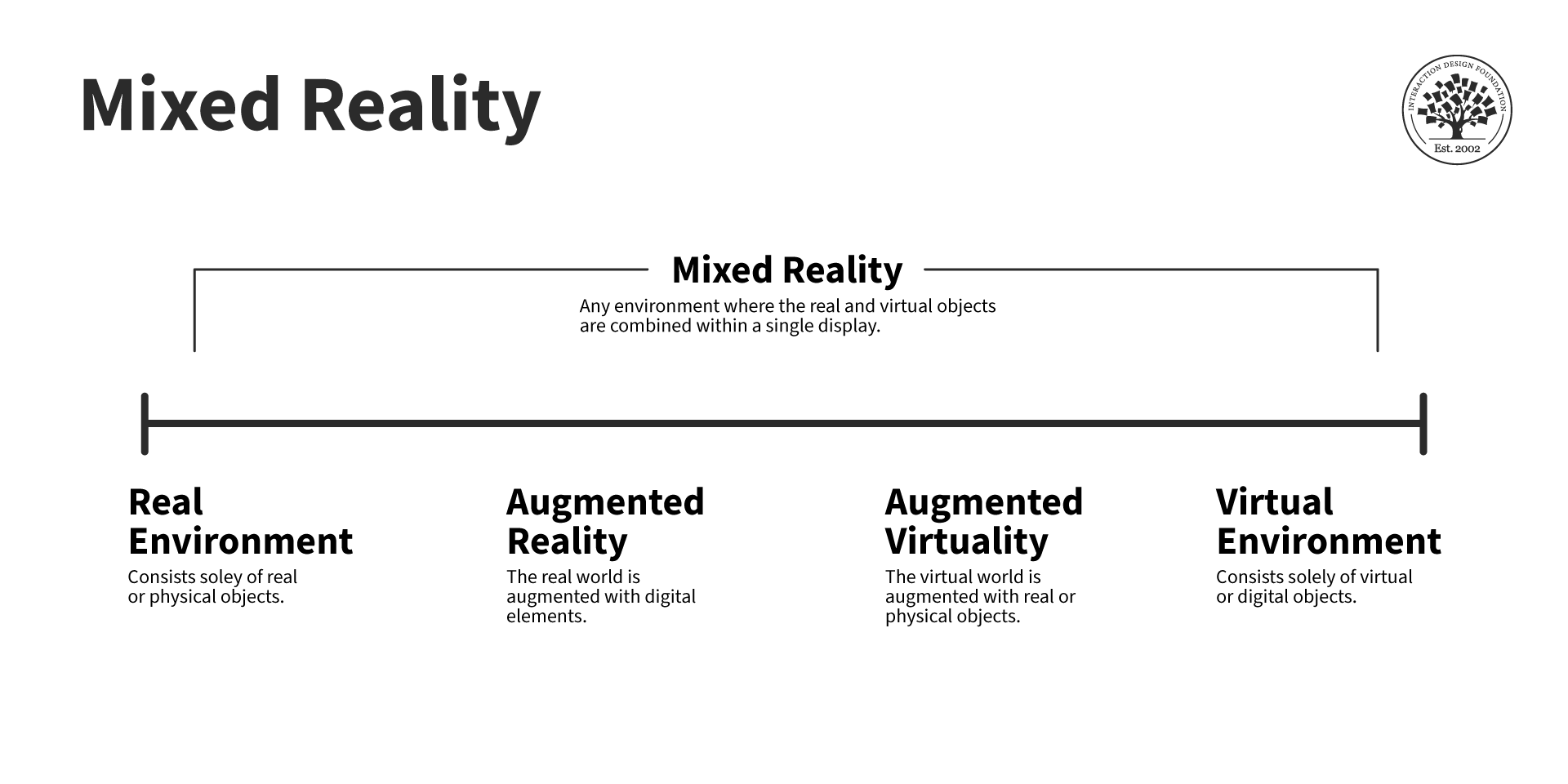 Source: Interaction Design Foundation
Source: Interaction Design Foundation
Their framework laid the foundation for today’s extended reality (XR) technologies, inspiring decades of innovation in immersive computing and visualization. Often referred to as “augmented reality 2.0,” mixed reality is driven by cutting-edge technologies that make digital experiences feel seamless, lifelike, and impossible to forget.
New hardware is defining the next chapter of MR. Companies are focused on improving comfort, visual clarity, and battery efficiency while integrating advanced spatial tracking and AI processing.
- Samsung Galaxy XR (Project Moohan): Samsung and Google’s long-anticipated mixed reality headset is slated for a 2025 release, combining Android XR with high-fidelity visuals and spatial awareness.
- Vivo Vision Headset: vivo’s first MR device focuses on lightweight design and improved optics, showing how Asian manufacturers are joining the XR race.
AI-driven spatial mapping, predictive rendering, and real-time environmental recognition are enhancing MR realism. Cloud-based rendering now enables cross-device MR experiences without high local computing power
Mixed reality is no longer confined to labs or enterprises. Improved affordability and intuitive UX are pushing MR toward everyday use, from home design and gaming to remote collaboration.
Developers are building interactive MR games that adapt to room layouts and allow multi-user experiences. Cloud-streamed MR titles are emerging, letting players join shared 3D environments without heavy hardware.
MR is proving its value in high-stakes industries. The US Army transferred its $22 billion MR headset program from Microsoft to defense tech firm Anduril, emphasizing MR’s strategic importance for situational training and field visualization.
Emerging technologies are improving how MR devices perceive movement and space. A 2025 study titled BodyWave: Egocentric Body Tracking using mmWave Radars on an MR Headset explores new forms of non-camera tracking for more private, accurate spatial input.
The XR ecosystem is heating up, with Meta, Apple, Samsung, Magic Leap, and Lenovo competing to define the next generation of spatial computing. 2025’s product lineup shows faster iteration cycles, cross-platform SDKs, and growing investment in immersive media.
It's safe to say that 2025 marks the year mixed reality moves from novelty to necessity. With smarter devices, stronger AI, and enterprise validation, MR is redefining how people visualize, learn, and collaborate, blending imagination with reality like never before.
Mixed reality: Frequently asked questions
Q1. Is mixed reality the same as the metaverse?
Not exactly. The metaverse is a shared virtual world where users interact through avatars. Mixed reality can be part of the metaverse, but it focuses on merging real and digital environments rather than replacing reality entirely.
Q2. Can mixed reality work without a headset?
Yes — some MR applications run on smartphones, tablets, or web browsers using camera-based spatial mapping, though headsets provide deeper immersion.
Q3. What skills are needed to develop MR experiences?
Developers typically need knowledge of 3D modeling, Unity or Unreal Engine, spatial computing, and programming languages like C# or C++.
Q4. What companies are leading MR innovation?
Major players include Microsoft (HoloLens), Magic Leap, Meta (Quest series), Apple (Vision Pro), and Lenovo (ThinkReality).
Q5. How secure is mixed reality data?
Because MR devices collect spatial and biometric data, security is critical. Encryption, local data processing, and user consent controls help protect sensitive information.
No mixed feelings here
Mixed reality has surely set humankind on an ambitious journey to explore more about the universe.
It’s just getting started, but a glimpse so far has had a drastic impact on people and their mindsets. In the coming years, we’ll get to see how everyone uses mixed reality in unison to work, play, and communicate their ideas.
Want to create your own immersive experiences? Explore top-rated 3D modeling software to design, render, and visualize the digital worlds of tomorrow.
.png?width=400&height=150&name=Copy%20of%20G2%20Image%20(1).png)




.png)





