July 14, 2023
 by Samudyata Bhat / July 14, 2023
by Samudyata Bhat / July 14, 2023

Data is at the core of businesses. Meeting customer needs, adapting to unexpected events, and responding to rapid market fluctuations ultimately depend on data.
Companies generate vast amounts of data from various sources. The sheer volume and granularity of data generated during business require constant attention to data protection and maintenance. After all, data is more than just a collection of static records.
Whether small or big, data protection must be at the forefront of considerations for any business. While solutions like data-centric security software ensure that the data stored within a database is secure and used properly, it is vital to understand what data protection is, how it works, and its related technologies and trends.
Data protection is the process of preventing critical information from being corrupted, compromised, or lost. A successful data protection strategy can help minimize damage caused by a breach or disaster.
The need for data protection grows as the quantity of data generated and saved expands at unprecedented rates. There is also minimal tolerance for downtime, which might make access to critical information impossible.
Consequently, ensuring that data can be recovered rapidly after corruption or loss is an essential aspect of a successful data protection strategy. Data protection also includes safeguarding data against compromise and preserving data privacy.
Data protection is crucial since it aids businesses in preventing data breaches, exfiltration, downtime, reputational harm, and financial loss. Organizations must also enforce data protection to restore lost or damaged data and comply with legal obligations.
This approach has become more critical as workforces become more volatile and run the danger of illicit data removal.
While object storage solutions house all sorts of data, businesses need data protection to address specific security issues. Although they can vary depending on the type of business, the following typical problems affect most businesses and can be avoided with data protection.
Data protection principles help preserve data and ensure its accessibility at all times. This includes adopting data management and availability elements, operational data backup, business continuity, and disaster recovery.
The following are the key data management principles of data protection:
There are several crucial distinctions between data privacy, data security, and data protection, even though these terms are often used interchangeably, as mentioned below:
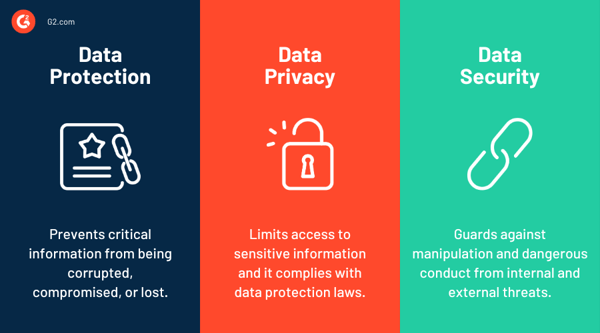
When working with departments outside of security, in particular, recognizing the differences between these terminologies can help avoid misunderstandings.
Data protection acts and laws govern the collection, transmission, and use of specific data types. Names, images, email addresses, account numbers, internet protocol (IP) addresses of personal computers, and biometric information are only a few examples of the many different forms of information that constitute personal data.
Different nations, jurisdictions, and sectors have different data protection and privacy laws. Depending on the infraction and the instructions provided by each legislation and regulatory body, non-compliance may result in reputational harm and financial penalties.
The observance of one set of rules does not imply adherence to all laws. All rules are susceptible to change, and each legislation has various provisions that can apply in one situation but not another. Given this complexity, implementing compliance consistently and acceptably is challenging.
Governments worldwide are focusing on data security and privacy legislation, which significantly influences how these systems work. Some prominent data protection acts are discussed below.
The General Data Protection Regulation is an EU regulation that was enacted in 2016. It allows individual users of digital services additional rights and control over the personal information they provide to companies and other organizations.
Businesses operating in or collaborating with EU nations that do not comply with these rules face hefty fines of up to 4% of their global sales or 20 million Euros.
In contrast to the EU, the U.S. lacks a single primary data protection law. Instead, hundreds of federal and state privacy regulations are intended to safeguard Americans' data. Below are some illustrations of such laws.
In the subsequent years, U.S. regulatory requirements may change as data protection becomes an increasingly important concern in a digital society.
In 2019, Australia implemented the Prudential Standard CPS 234 to govern how financial and insurance businesses defend their information security from cyber attacks. It also necessitates the implementation of tight auditing and reporting mechanisms to guarantee that systems remain compliant.
No matter how big or small an organization is, processing personal data is at the heart of all its operations. The list below reasons out the benefits of data protection.
The downsides of data protection during the implementation of data protection strategies are discussed below.
As computing environments change, several fresh trends impact the data protection landscape. A few of these include the following.
Manual labor has become increasingly unstable since COVID-19, and people change jobs frequently. Numerous factors have led to high turnover in companies:
Because of the unpredictable nature of the workforce, there is now a greater danger that departing employees may take data with them, either intentionally or out of a sense of ownership over their work.
Security teams have become more critical in creating new data protection methods in response to this increased danger of data exfiltration. Training measures, in addition to monitoring and risk management, are also vital to ensure personnel are aware of which data is not legally theirs to store.
A hyper-converged infrastructure combines storage, computation, and networking into a single system. Instead of handling the complexities of dispersed hardware and resources, IT managers may communicate under this paradigm with a single interface, generally through virtual machines (VMs).
From the data safety standpoint, hyper convergence's benefit decreases the surface area the security team must control. Furthermore, it can automate much of the complexity associated with resource allocation, data duplication, and backups.
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts vital data, making it inaccessible to users. It usually demands a ransom payment from the victim to the attacker to unlock the data. This practice forces the victim to choose between losing data and paying a considerable ransom without guaranteeing that the attacker will solve the problem.
Businesses may use ransomware prevention solutions to monitor specific malware entry points, such as phishing campaigns. These solutions can also aid in isolating infected devices, preventing lateral movement, and reducing the attack surface area.
A zero-trust security model or architecture requires all users to authenticate when accessing internal applications, data, and servers.
In a zero-trust system, traffic is not assumed to originate from a trusted source, unlike a typical network that relies primarily on firewalls to protect an isolated network.
Organizations no longer trust cloud applications and remote workers within a secure local network, so the zero-trust paradigm is becoming increasingly critical for modern data protection. Systems must also use other types of authentication, such as single sign-on (SSO) and user access control, to authenticate users and prevent unauthorized access.
Since data protection concerns security measures, availability, and administration, numerous technologies exist to assist businesses in achieving these objectives. A few of them are discussed below.
Understanding all of the technologies available for data protection can help determine which solution is appropriate for your business.
Data protection is critical for organizations to manage risk, increase service uptime, and avoid data loss or abuse. To achieve these objectives, however, all files, vectors, and user activity must be monitored without interfering with employee cooperation and productivity.
Data-centric security solutions are used by businesses to secure data that transfers between places, such as on-premises to cloud storage, between numerous apps, or to third parties. Furthermore, these technologies make it easier to identify, classify, and monitor sensitive data points and audits for security and compliance assurance.
* Above are the top 5 data-centric security service providers per G2’s Fall 2024 Grid® Report.
A Data Protection Officer (DPO) is responsible for ensuring an organization complies with data protection laws and oversees data processing activities to protect personal data.
Cloud data protection involves securing data stored in the cloud through encryption, access controls, backups, and compliance with regulations to prevent unauthorized access and data loss.
Virtualization allows for easy backup, replication, and recovery of data and systems, making it quicker and more efficient to restore operations after a disaster.
A Data Protection Authority (DPA) is an independent body that enforces data protection laws, monitors compliance, and protects individuals' privacy rights.
Establishing a thorough understanding of and enforcing good data practices (e.g., guaranteeing that data is not just physically protected but also that users understand how it may be used) combined with protection that backs that up allows data to be more valuable.
Organizations produce quintillion bytes of data every day. Therefore, it makes sense that they are always looking for improved data management technologies. Data protection, after all, is a part of overall data management.
Want to understand data better? Learn more about data as a service (DaaS) and how it's relevant today!
Samudyata Bhat is a former Content Marketing Specialist at G2. With a Master's degree in digital marketing, she specializes her content around SaaS, hybrid cloud, network management, and IT infrastructure. She aspires to connect with present-day trends through data-driven analysis and experimentation and create effective and meaningful content. In her spare time, she can be found exploring unique cafes and trying different types of coffee.
If you’re working hard to protect and save your data, you want to make sure you’re employing...
 by Alexa Drake
by Alexa Drake
News of a major data breach seems almost commonplace.
 by Mara Calvello
by Mara Calvello
Regardless of your industry, your business's data needs protection. This is especially true as...
 by Holly Landis
by Holly Landis
If you’re working hard to protect and save your data, you want to make sure you’re employing...
 by Alexa Drake
by Alexa Drake
News of a major data breach seems almost commonplace.
 by Mara Calvello
by Mara Calvello


