April 24, 2023
 by Jeremy Moser / April 24, 2023
by Jeremy Moser / April 24, 2023

Selling SaaS products is no different than selling any other product.
The sales industry is the same everywhere, right?
Not exactly.
To succeed in SaaS sales, you need a dedicated, knowledgeable team that understands the SaaS sales cycle and can create value around your brand. But it’s a lot easier said than done. In a SaaS landscape, you not only have to incentivize your team to succeed but also create a winning sales strategy to predict successes or failures.
If you're trying to assemble the best possible SaaS team and unsure where to start, you're in the right place. This article explains how SaaS sales differs from other sales industries, the SaaS cycle, and how to strategize and sell SaaS effectively.
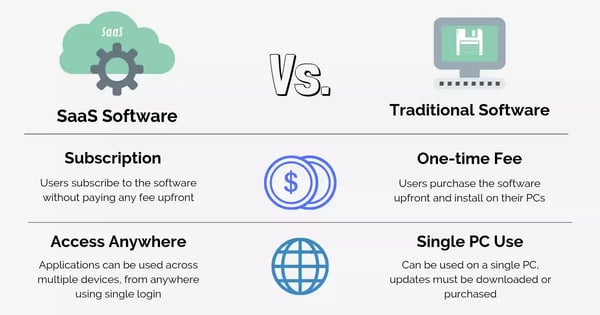
SaaS sales is the process of selling software as a service (SaaS) on a subscription-based model. SaaS is a cloud-based software delivery model where software applications are hosted on a third-party server and accessed over the internet.
The SaaS sales process heavily focuses on acquiring new customers. With proactive prospecting and advertising, you're constantly adding new users to your pipeline. But SaaS isn't a service that customers buy just once.
The industry operates on a subscription pricing model, making retention and upselling critical to continued success. You want to sell annual plans whenever possible and ensure your customers sign up again at the end of the commitment period.
Unlike traditional software, SaaS solutions are typically priced high. Pricing isn't your selling point for SaaS, but the value of your product is. The better your offering, the better your chances of attracting and retaining a SaaS audience.
Source: Imaginovation
Customers use SaaS solutions within set terms. Since third-party companies engineer these products, customer support is usually readily available and proactive.
If you purchase a traditional product and something goes wrong, you’ll have to repair it yourself. But since SaaS products are online, skilled technicians keep the service running smoothly and up-to-date with the latest technology and security. This removes the need for tardy technical maintenance.
Another major difference between SaaS and traditional sales is pricing. SaaS purchase requires time and careful consideration, which results in a longer-than-average sales cycle and a high purchase cost.
In SaaS sales, sales-qualified leads (SQLs) aren’t necessarily ready for conversion or even a demo. These customers require more nurturing than other industries, which adds extra touchpoints to the sales cycle.
The SaaS sales process is built on the capabilities of a particular software and how well you present it. Selling SaaS requires closer alignment and coordination between sales, marketing, and engineering, given the technicalities involved.
Only engineers and other experts are equipped to answer key technical questions about the software products. Working closely with engineering, sales and marketing can better inform customers. When customers get the right support, they stay with you. This improves customer loyalty and promotes long-term business success.
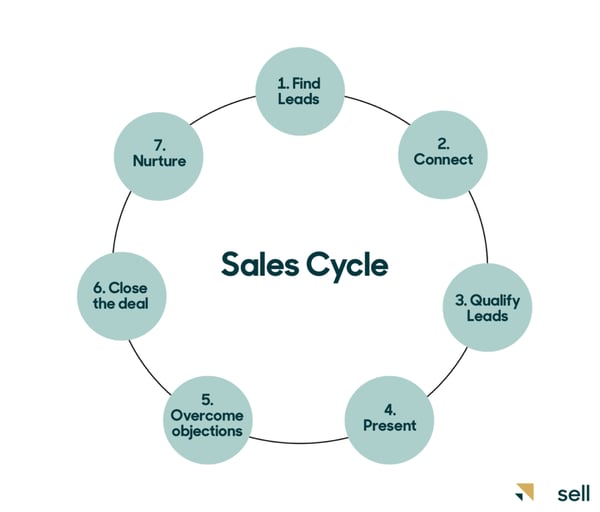
The SaaS sales cycle varies based on the SaaS product's complexity, target audience, and pricing.
Source: Zendesk
SaaS sales cycles can vary depending on the type of product, target audience, and the sales process' complexity. The more expensive the product, the longer the sales cycle. Let's take an example.
If pricing for a task management software starts at $5 per user per month, many freelancers and small businesses can use this tool to keep track of their daily to-do lists. Their pricing and consumer base type make their sales cycle faster.
Now compare this to a more expensive product. If an SEO content optimization tool costs up to $12,000 annually, it attracts an enterprise audience that employs multiple steps to add tools to its tech stack. Such a product inevitably has a longer sales cycle.
However, a typical SaaS sales cycle usually follows a few general stages.Typically, SaaS companies with annual contract value (ACV) under $5,000 have an average sales cycle of 40 days. All annual contracts priced over $100,000 typically last up to 170 days. However, the average length of the SaaS sales cycle is close to 84 days.
The SaaS sales cycle depends on the following factors:
Selling SaaS can be lucrative but requires a unique approach compared to traditional software sales—in-depth understanding of the product, the target market, and sales techniques.
To successfully sell SaaS, consider these key strategies and best practices.
A demo is a small sample of your product that demonstrates its value. It’s a one-time experience, often conducted under supervision.
Demos help customers better understand what they’re paying for. A best practice when delivering demos is not to overwhelm prospects with too much information.
If you rush to roll out all your features at once, customers could get confused and pass on the product. Instead, use your time wisely and show them specific features that alleviate their biggest pain points.
Offer trial periods to attract new customers and build trust. A trial period grants prospects partial or full access to your solution for a set period, usually ranging from a few days to weeks. It's the perfect time for prospects to test your offering and assess whether it meets their needs.
From the company's perspective, it's an opportunity to acquire new customers, identify pain points, and overcome objections. By monitoring usage patterns and collecting feedback, you can see how prospects use your products and where they encounter problems or obstacles. This information will help improve the product, refine the sales pitch, and optimize the customer experience.
Tip: A long trial period adds time to your sales cycle and factors into sales projections. Be mindful of your sales cycle before offering a trial period.
Find opportunities to upsell or cross-sell to existing customers. At lower subscription levels, see if customers could take advantage of more features and accessibility. This is the perfect time to suggest an upgrade.
To upsell or cross-sell effectively, identify opportunities with existing customers. For example, a customer who used a SaaS product with a lower subscription tier might be ready for more features or accessibility. This is the perfect time to propose an upgrade and highlight the benefits of the higher tier subscription and how it fits the customer's needs.
You can also sell complementary products or services. For example, a company that offers project management software could cross-sell a time-tracking tool to its existing customers. This generates additional revenue and enhances customer relationships. Customers perceive you as a one-stop shop for all their software needs.
Upselling and cross-selling require you to better understand your customer's needs and preferences. With these selling techniques, you can increase revenue, improve customer satisfaction, and strengthen your position in the market.
Devising the right sales strategy is key to selling SaaS. So how do you begin?
Customer success isn’t an easy feat. You need the right metrics to track performance and optimize your sales strategy.
Let's look at some of these key metrics.
We've talked about the SaaS sales cycle, strategy, and metrics, but what about the people who actually work in this industry?
SaaS is a lucrative field for the right person. The base salary and commission rates are typically higher than the national average. As a SaaS sales rep, it's imperative you understand the intricacies of software sales, which requires extensive specialized training. The sales cycle length also determines how much a sales rep would make.
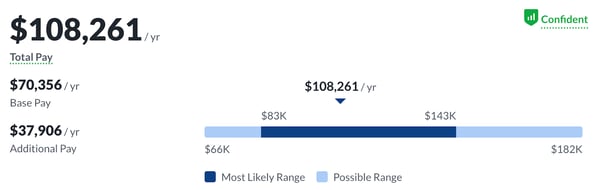
According to Glassdoor, the average base salary for a SaaS salesperson is $70,456 per year. In addition, they typically see commissions of around $37,876 per year. This brings the average total gross salary for a SaaS salesperson to $108,332 per year.
Source: Glassdoor
Other sales industries offer an average base salary of $57,975 with commissions of around $30,421 for a total salary of $88,396. Compensation is a major driver for SaaS sales professionals. With nearly 40% of employees’ main concern being keeping wages below inflation, a key driver is competitive and fair pay.
You’ll want to offer competitive salaries that meet industry norms to attract top talent. Some companies are trying to use Gates to incentivize larger commissions. Gates ensures there are no incentives for exceeding sales targets unless key metrics are met, such as first-call resolution, attendance, and customer satisfaction score (CSAT).
For a field as specialized as SaaS, reps might or might not need prior specialized experience or high-level training. The average SaaS salesperson starts with absolutely no experience. On-the-job training educates them about various products and services and the SaaS sales cycle.
This is quite different from many other industries. For example, a life insurance company typically hires salespeople with prior experience in insurance sales. Similarly, in medical technology, you may want someone with experience in the medical industry, either from a sales perspective or someone who has worked in the industry and is looking for a career change.
This isn’t the case for entry-level SaaS sales positions. Most SaaS companies prefer to train their sales team from scratch, with many requiring no sales experience. Teaching someone a preferred method is much easier than having them unlearn it.
However, that doesn't mean SaaS sales teams don't need training. In fact, they go through rigorous sales training that introduces them to the SaaS sales cycle and software-specific training to answer technical and specific customer questions.
Selling SaaS is complex but potentially lucrative. Sales reps enjoy a comfortable life while learning on the job and making profits for their business.
All it takes is the right team that stays resilient and takes your business to the next level.
Stay ahead of the game and learn about the latest SaaS trends that'll help you gain an edge in a competitive SaaS world.
Jeremy is the co-founder & CEO at uSERP, a digital PR and SEO agency. He also buys and builds SaaS companies like Wordable and writes for publications like Entrepreneur and Search Engine Journal.
Product-led growth (PLG) is a go-to-market strategy that centers on the product.
 by Ioana Sima
by Ioana Sima
Selling SaaS is not a sprint; it’s a marathon.
 by Sameer Sinha
by Sameer Sinha
Traditionally, sales couldn’t be scaled unless you hired more salespeople or marketers, and...
 by Mehdi Hussen
by Mehdi Hussen
Product-led growth (PLG) is a go-to-market strategy that centers on the product.
 by Ioana Sima
by Ioana Sima
Selling SaaS is not a sprint; it’s a marathon.
 by Sameer Sinha
by Sameer Sinha


