When you read the word “gig,” another word probably comes to mind: "temporary."
This is the foundation on which the gig economy is based. While the concept of a “side hustle” is not new, the age of digital transformation has created a quick path to short-term jobs. This is colloquially referred to as the gig economy.
What is the gig economy?
Before we go into what the gig economy is, let’s start with the definition.
Gig economy definition
The gig economy is a labor market distinguished by workers that take short-term contracts or freelance work as opposed to permanent jobs.
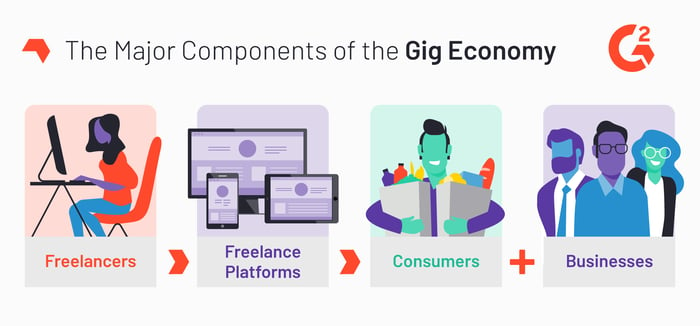
Freelancers attract consumers by providing goods or services. Examples of services providers include, but are not limited to, handymen, drivers and cleaning services. Workers that provide on-demand goods might be artists, photographers or writers.
Freelancers are independent workers that perform temporary jobs or projects for consumers. Unsurprisingly, freelancers are the main component that keeps the gig economy moving. The other major component of the gig economy is the connection between freelancers, and consumers and businesses. Most commonly, the two groups are connected through freelance platforms, which essentially act as a freelancer marketplace. They also facilitate transactions between freelancers and their clients.

What are the benefits of the gig economy?
The gig economy has many benefits that drive its growing popularity. Job flexibility is the driving force that keeps the gig economy flourishing.
Freelancers are free to establish their preferences and expectations before taking on a new job or project. They can also independently negotiate their wages. For anyone seeking to become their own boss, freelancing is an optimal route.
Temporary work is also a great option for those that dislike a traditional routine. Freelancers can choose a variety of projects, so the work can vary greatly. Additionally, they can set their own hours, pay, and, occasionally, deadlines. This flexibility is key for people that have irregular schedules, multiple jobs, or simply enjoy making their own schedule.
What are the disadvantages of the gig economy?
Not everything in the gig economy is positive. One of the major disadvantages is the lack of benefits. While more businesses are including comprehensive benefits packages for freelancers, there’s a long way to go before it becomes the norm. For freelancers that don’t have benefits, the Freelancer Union offers resources to help them independently set up insurance, a retirement account and more.
Another disadvantage is the extra hassle involved with taxes, payroll and independent decision-making. A typical employee gets their taxes withdrawn from their paycheck, making tax season a bit less daunting than it is for entrepreneurs. Freelancers rely on income tracking and tax preparation apps to keep track of their taxes and the paperwork involved, which can be stressful. Furthermore, while the independence of freelancing is a perk, it is also a burden.
Freelancers must stay up to date with the average pay bands in their field. If their requested pay rate is too high, they’re less likely to get hired. If their requested pay is too low, they’re missing out on deserved revenue.
How the gig economy is influencing businesses
Businesses have a lot to gain from the gig economy. Freelancers are a great choice for companies with temporary or urgent projects. Freelancers let businesses hire a one-off employee with no long-term commitment as quickly as possible.
Businesses with a global market also rely on freelancers. As long as the work can be done remotely, businesses can hire freelancers around the world, making round-the-clock work possible. For example, a global retailer based in the U.S. might want to hire customer service representatives in different time zones so customers can always get in touch.
The ability to hire globally is a perk in itself. It expands the pool of job applicants with diverse skills.
Hiring freelancers is also more cost-effective. Onboarding a new, full-time employee can be pricey. With freelancers, businesses don’t need to buy new equipment or spend money on benefits and other onboarding expenses.
How people are finding jobs in the gig economy
According to Forbes, 57 million Americans are part of the gig economy. That’s more than one-third of the population. So, how are these workers finding their jobs? Many gig workers find jobs by traditional networking, connecting with old jobs or coworkers, and using social media. However, freelance platforms have been disrupting these methods.
According to the MBO Partners 2018 State of Independence Report, 22% of full-time freelancers said they plan to use a freelance platform over the next 12 months. Additionally, millennials are three times more likely to use online platforms to find work than baby boomers. Freelance platforms are appealing, as they streamline the job-seeking process on a single platform.
The future of the gig economy
As freelancing becomes easier and more lucrative, the number of freelancers is expected to grow. With that in mind, the gig economy is still developing. It has a long way to go for it to become as stable as a typical 9-to-5 job. Freelancing is essentially being your own boss, which has plenty of advantages and setbacks to consider. For anyone looking to dip their toes into entrepreneurship, freelancing is a good start.
 by Tricia Dempsey
by Tricia Dempsey
 by Tricia Dempsey
by Tricia Dempsey
 by Alina Benny
by Alina Benny